Alejandro Monroy Muñoz
DuoDiff: Accelerating Diffusion Models with a Dual-Backbone Approach
Oct 12, 2024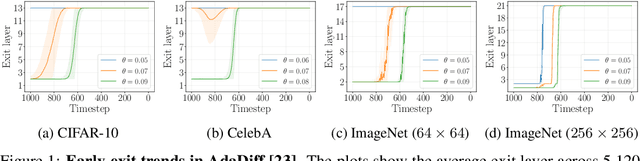
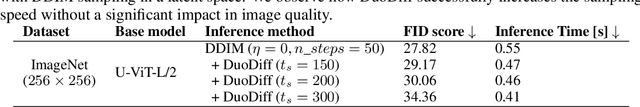
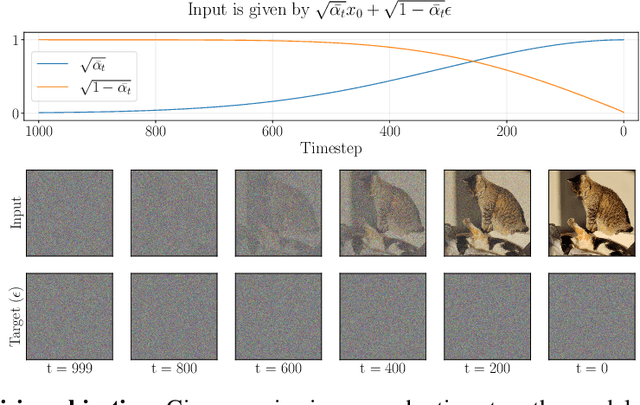
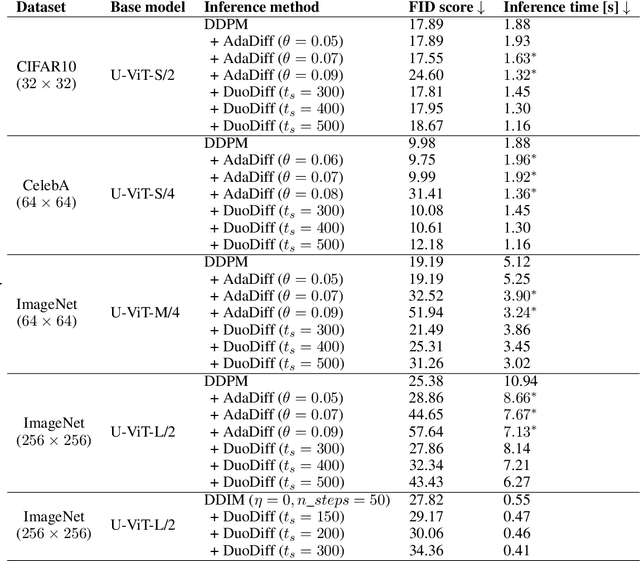
Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved unprecedented performance in image generation, yet they suffer from slow inference due to their iterative sampling process. To address this, early-exiting has recently been proposed, where the depth of the denoising network is made adaptive based on the (estimated) difficulty of each sampling step. Here, we discover an interesting "phase transition" in the sampling process of current adaptive diffusion models: the denoising network consistently exits early during the initial sampling steps, until it suddenly switches to utilizing the full network. Based on this, we propose accelerating generation by employing a shallower denoising network in the initial sampling steps and a deeper network in the later steps. We demonstrate empirically that our dual-backbone approach, DuoDiff, outperforms existing early-exit diffusion methods in both inference speed and generation quality. Importantly, DuoDiff is easy to implement and complementary to existing approaches for accelerating diffusion.
Reproducibility Study of "ITI-GEN: Inclusive Text-to-Image Generation"
Jul 29, 2024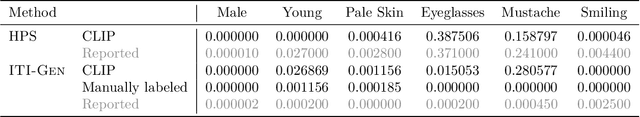

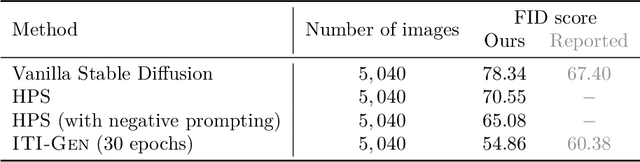

Abstract:Text-to-image generative models often present issues regarding fairness with respect to certain sensitive attributes, such as gender or skin tone. This study aims to reproduce the results presented in "ITI-GEN: Inclusive Text-to-Image Generation" by Zhang et al. (2023a), which introduces a model to improve inclusiveness in these kinds of models. We show that most of the claims made by the authors about ITI-GEN hold: it improves the diversity and quality of generated images, it is scalable to different domains, it has plug-and-play capabilities, and it is efficient from a computational point of view. However, ITI-GEN sometimes uses undesired attributes as proxy features and it is unable to disentangle some pairs of (correlated) attributes such as gender and baldness. In addition, when the number of considered attributes increases, the training time grows exponentially and ITI-GEN struggles to generate inclusive images for all elements in the joint distribution. To solve these issues, we propose using Hard Prompt Search with negative prompting, a method that does not require training and that handles negation better than vanilla Hard Prompt Search. Nonetheless, Hard Prompt Search (with or without negative prompting) cannot be used for continuous attributes that are hard to express in natural language, an area where ITI-GEN excels as it is guided by images during training. Finally, we propose combining ITI-GEN and Hard Prompt Search with negative prompting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge