Alberto Rigo
Hierarchical Optimization-based Control for Whole-body Loco-manipulation of Heavy Objects
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:In recent years, the field of legged robotics has seen growing interest in enhancing the capabilities of these robots through the integration of articulated robotic arms. However, achieving successful loco-manipulation, especially involving interaction with heavy objects, is far from straightforward, as object manipulation can introduce substantial disturbances that impact the robot's locomotion. This paper presents a novel framework for legged loco-manipulation that considers whole-body coordination through a hierarchical optimization-based control framework. First, an online manipulation planner computes the manipulation forces and manipulated object task-based reference trajectory. Then, pose optimization aligns the robot's trajectory with kinematic constraints. The resultant robot reference trajectory is executed via a linear MPC controller incorporating the desired manipulation forces into its prediction model. Our approach has been validated in simulation and hardware experiments, highlighting the necessity of whole-body optimization compared to the baseline locomotion MPC when interacting with heavy objects. Experimental results with Unitree Aliengo, equipped with a custom-made robotic arm, showcase its ability to successfully lift and carry an 8kg payload and manipulate doors.
Contact Optimization for Non-Prehensile Loco-Manipulation via Hierarchical Model Predictive Control
Oct 07, 2022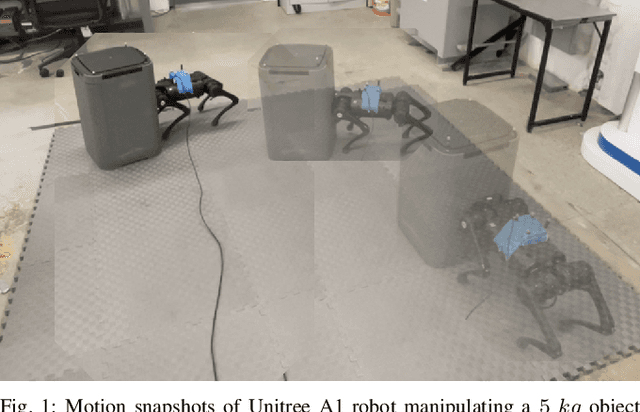
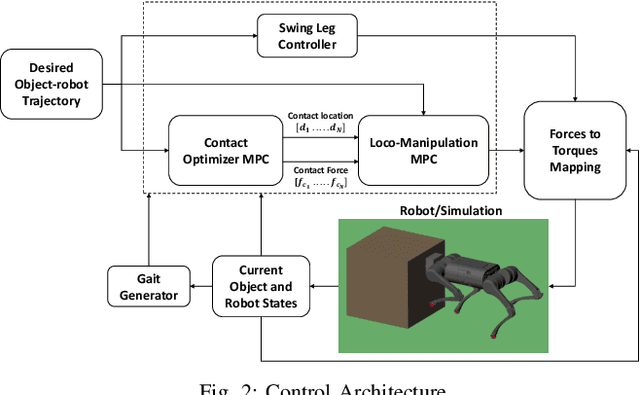
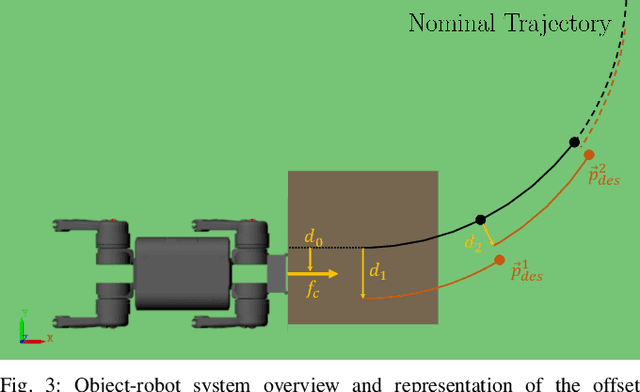
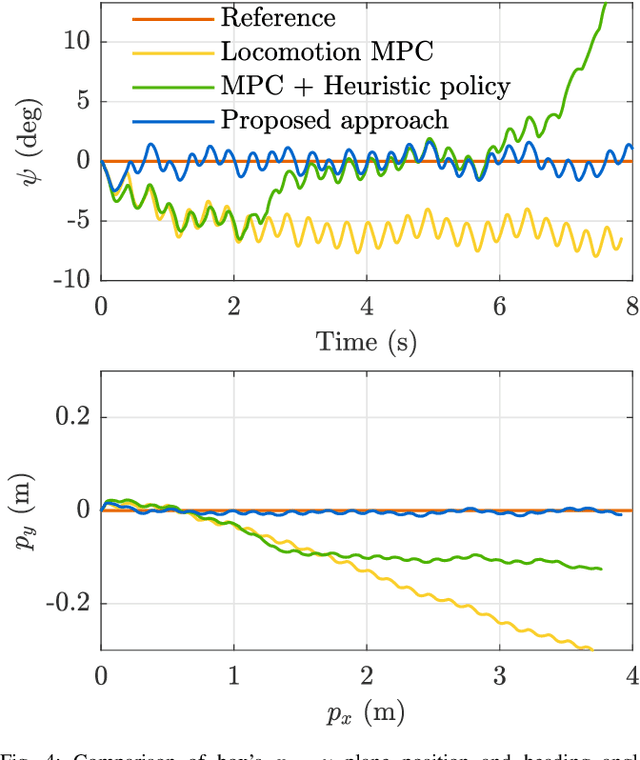
Abstract:Recent studies on quadruped robots have focused on either locomotion or mobile manipulation using a robotic arm. Legged robots can manipulate heavier and larger objects using non-prehensile manipulation primitives, such as planar pushing, to drive the object to the desired location. In this paper, we present a novel hierarchical model predictive control (MPC) for contact optimization of the manipulation task. Using two cascading MPCs, we split the loco-manipulation problem into two parts: the first to optimize both contact force and contact location between the robot and the object, and the second to regulate the desired interaction force through the robot locomotion. Our method is successfully validated in both simulation and hardware experiments. While the baseline locomotion MPC fails to follow the desired trajectory of the object, our proposed approach can effectively control both object's position and orientation with minimal tracking error. This capability also allows us to perform obstacle avoidance for both the robot and the object during the loco-manipulation task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge