Alavikunhu Panthakkan
Advanced Deep Learning Approaches for Automated Recognition of Cuneiform Symbols
May 07, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a thoroughly automated method for identifying and interpreting cuneiform characters via advanced deep-learning algorithms. Five distinct deep-learning models were trained on a comprehensive dataset of cuneiform characters and evaluated according to critical performance metrics, including accuracy and precision. Two models demonstrated outstanding performance and were subsequently assessed using cuneiform symbols from the Hammurabi law acquisition, notably Hammurabi Law 1. Each model effectively recognized the relevant Akkadian meanings of the symbols and delivered precise English translations. Future work will investigate ensemble and stacking approaches to optimize performance, utilizing hybrid architectures to improve detection accuracy and reliability. This research explores the linguistic relationships between Akkadian, an ancient Mesopotamian language, and Arabic, emphasizing their historical and cultural linkages. This study demonstrates the capability of deep learning to decipher ancient scripts by merging computational linguistics with archaeology, therefore providing significant insights for the comprehension and conservation of human history.
Evaluation of UAV-Based RGB and Multispectral Vegetation Indices for Precision Agriculture in Palm Tree Cultivation
May 06, 2025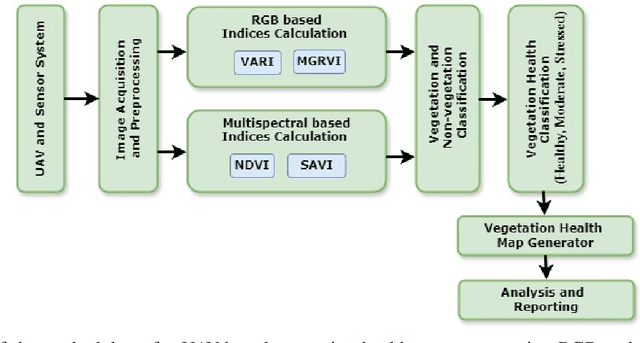

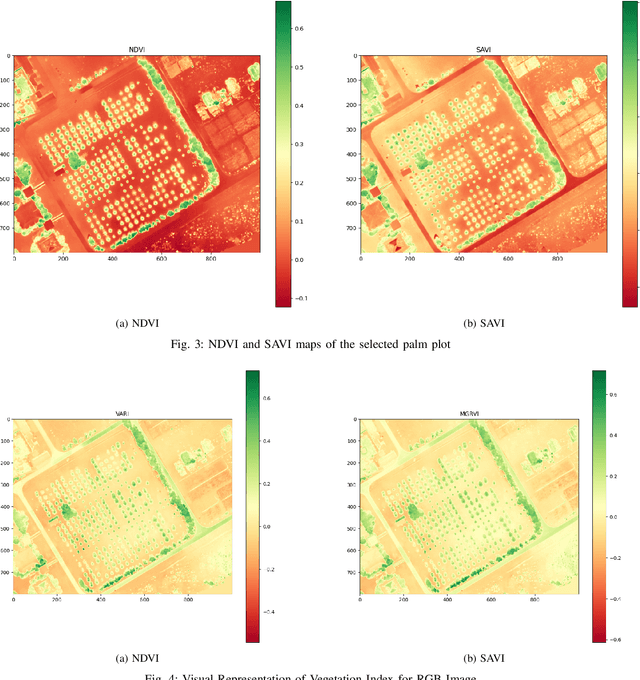
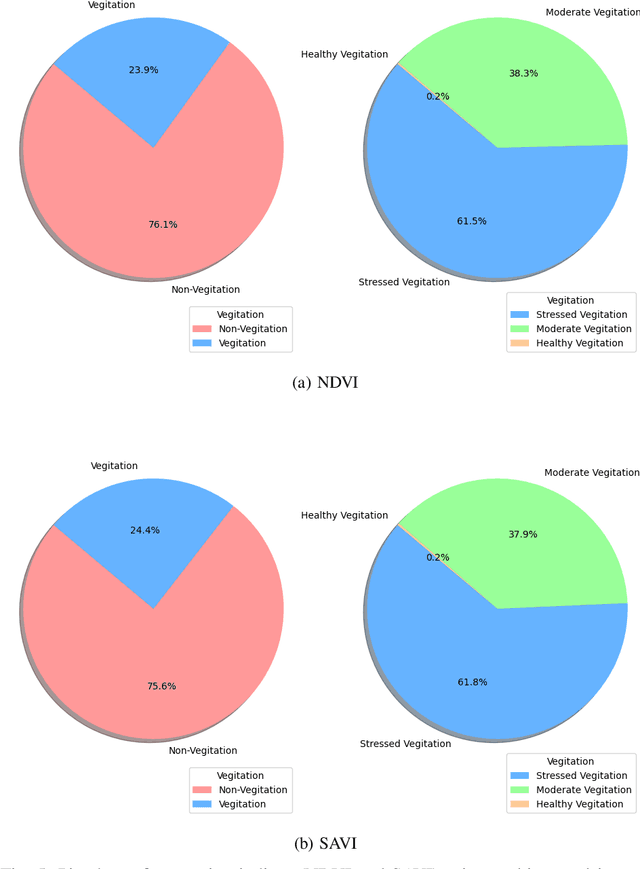
Abstract:Precision farming relies on accurate vegetation monitoring to enhance crop productivity and promote sustainable agricultural practices. This study presents a comprehensive evaluation of UAV-based imaging for vegetation health assessment in a palm tree cultivation region in Dubai. By comparing multispectral and RGB image data, we demonstrate that RGBbased vegetation indices offer performance comparable to more expensive multispectral indices, providing a cost-effective alternative for large-scale agricultural monitoring. Using UAVs equipped with multispectral sensors, indices such as NDVI and SAVI were computed to categorize vegetation into healthy, moderate, and stressed conditions. Simultaneously, RGB-based indices like VARI and MGRVI delivered similar results in vegetation classification and stress detection. Our findings highlight the practical benefits of integrating RGB imagery into precision farming, reducing operational costs while maintaining accuracy in plant health monitoring. This research underscores the potential of UAVbased RGB imaging as a powerful tool for precision agriculture, enabling broader adoption of data-driven decision-making in crop management. By leveraging the strengths of both multispectral and RGB imaging, this work advances the state of UAV applications in agriculture, paving the way for more efficient and scalable farming solutions.
Remote Sensing Based Crop Health Classification Using NDVI and Fully Connected Neural Networks
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Accurate crop health monitoring is not only essential for improving agricultural efficiency but also for ensuring sustainable food production in the face of environmental challenges. Traditional approaches often rely on visual inspection or simple NDVI measurements, which, though useful, fall short in detecting nuanced variations in crop stress and disease conditions. In this research, we propose a more sophisticated method that leverages NDVI data combined with a Fully Connected Neural Network (FCNN) to classify crop health with greater precision. The FCNN, trained using satellite imagery from various agricultural regions, is capable of identifying subtle distinctions between healthy crops, rust-affected plants, and other stressed conditions. Our approach not only achieved a remarkable classification accuracy of 97.80% but it also significantly outperformed conventional models in terms of precision, recall, and F1-scores. The ability to map the relationship between NDVI values and crop health using deep learning presents new opportunities for real-time, large-scale monitoring of agricultural fields, reducing manual efforts, and offering a scalable solution to address global food security.
Enhanced Hybrid Deep Learning Approach for Botnet Attacks Detection in IoT Environment
Feb 10, 2025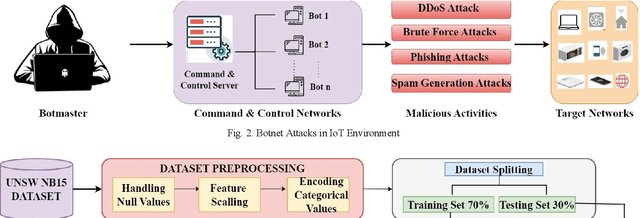
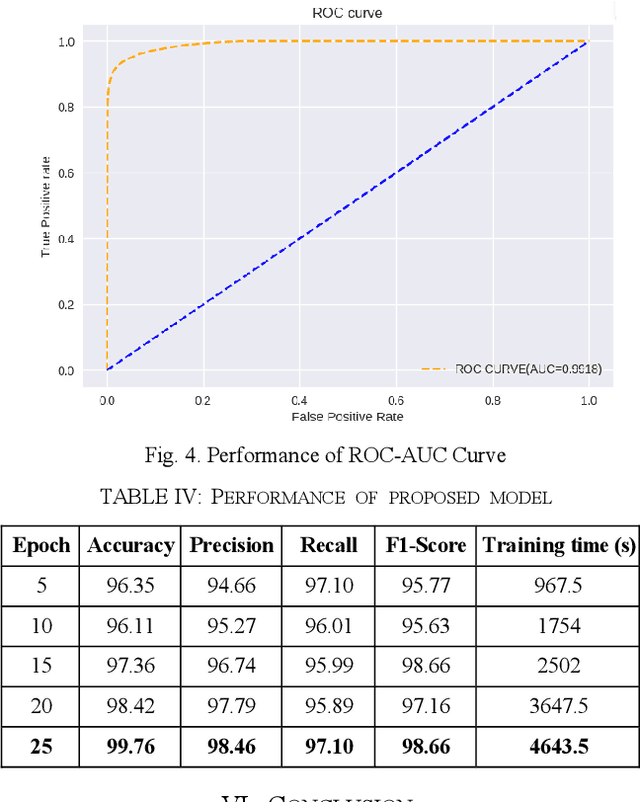
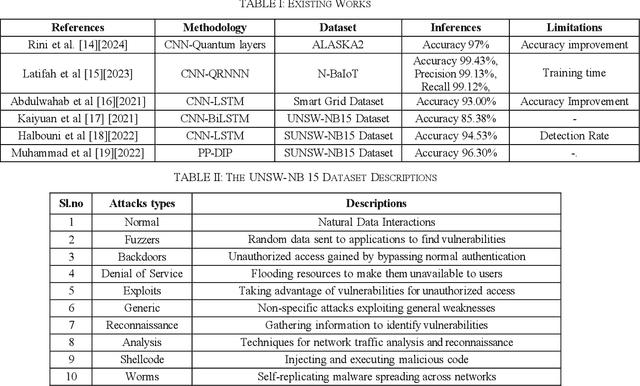
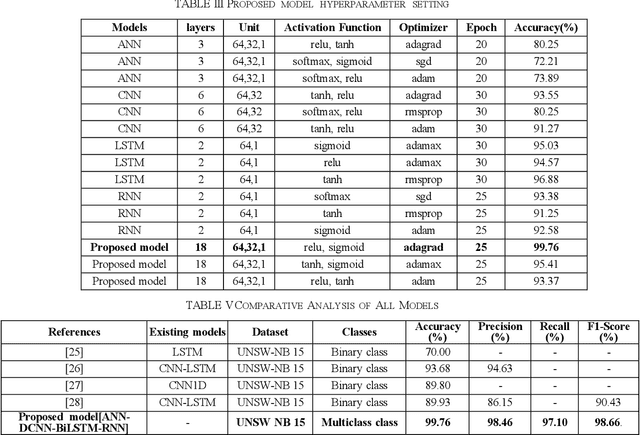
Abstract:Cyberattacks in an Internet of Things (IoT) environment can have significant impacts because of the interconnected nature of devices and systems. An attacker uses a network of compromised IoT devices in a botnet attack to carry out various harmful activities. Detecting botnet attacks poses several challenges because of the intricate and evolving nature of these threats. Botnet attacks erode trust in IoT devices and systems, undermining confidence in their security, reliability, and integrity. Deep learning techniques have significantly enhanced the detection of botnet attacks due to their ability to analyze and learn from complex patterns in data. This research proposed the stacking of Deep convolutional neural networks, Bi-Directional Long Short-Term Memory (Bi-LSTM), Bi-Directional Gated Recurrent Unit (Bi-GRU), and Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) for botnet attacks detection. The UNSW-NB15 dataset is utilized for botnet attacks detection. According to experimental results, the proposed model accurately provides for the intricate patterns and features of botnet attacks, with a testing accuracy of 99.76%. The proposed model also identifies botnets with a high ROC-AUC curve value of 99.18%. A performance comparison of the proposed method with existing state-of-the-art models confirms its higher performance. The outcomes of this research could strengthen cyber security procedures and safeguard against new attacks.
AI-Driven Solutions for Falcon Disease Classification: Concatenated ConvNeXt cum EfficientNet AI Model Approach
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Falconry, an ancient practice of training and hunting with falcons, emphasizes the need for vigilant health monitoring to ensure the well-being of these highly valued birds, especially during hunting activities. This research paper introduces a cutting-edge approach, which leverages the power of Concatenated ConvNeXt and EfficientNet AI models for falcon disease classification. Focused on distinguishing 'Normal,' 'Liver,' and 'Aspergillosis' cases, the study employs a comprehensive dataset for model training and evaluation, utilizing metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and f1-score. Through rigorous experimentation and evaluation, we demonstrate the superior performance of the concatenated AI model compared to traditional methods and standalone architectures. This novel approach contributes to accurate falcon disease classification, laying the groundwork for further advancements in avian veterinary AI applications.
Performance Evaluation of Image Enhancement Techniques on Transfer Learning for Touchless Fingerprint Recognition
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Fingerprint recognition remains one of the most reliable biometric technologies due to its high accuracy and uniqueness. Traditional systems rely on contact-based scanners, which are prone to issues such as image degradation from surface contamination and inconsistent user interaction. To address these limitations, contactless fingerprint recognition has emerged as a promising alternative, providing non-intrusive and hygienic authentication. This study evaluates the impact of image enhancement tech-niques on the performance of pre-trained deep learning models using transfer learning for touchless fingerprint recognition. The IIT-Bombay Touchless and Touch-Based Fingerprint Database, containing data from 200 subjects, was employed to test the per-formance of deep learning architectures such as VGG-16, VGG-19, Inception-V3, and ResNet-50. Experimental results reveal that transfer learning methods with fingerprint image enhance-ment (indirect method) significantly outperform those without enhancement (direct method). Specifically, VGG-16 achieved an accuracy of 98% in training and 93% in testing when using the enhanced images, demonstrating superior performance compared to the direct method. This paper provides a detailed comparison of the effectiveness of image enhancement in improving the accuracy of transfer learning models for touchless fingerprint recognition, offering key insights for developing more efficient biometric systems.
Analysing Osteoporosis Detection: A Comparative Study of CNN and FNN
Oct 11, 2024
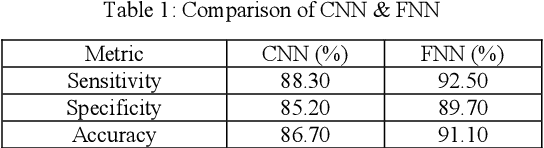
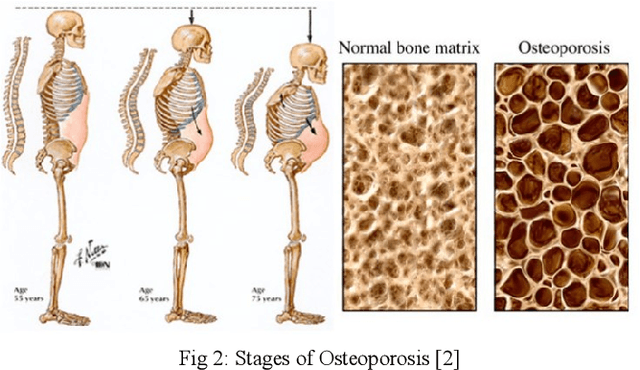
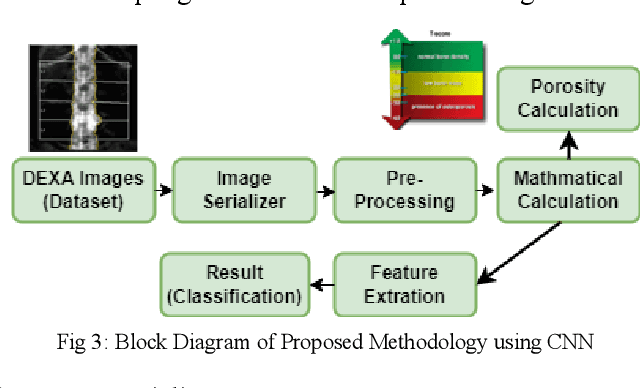
Abstract:Osteoporosis causes progressive loss of bone density and strength, causing a more elevated risk of fracture than in normal healthy bones. It is estimated that some 1 in 3 women and 1 in 5 men over the age of 50 will experience osteoporotic fractures, which poses osteoporosis as an important public health problem worldwide. The basis of diagnosis is based on Bone Mineral Density (BMD) tests, with Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) being the most common. A T-score of -2.5 or lower defines osteoporosis. This paper focuses on the application of medical imaging analytics towards the detection of osteoporosis by conducting a comparative study of the efficiency of CNN and FNN in DEXA image analytics. Both models are very promising, although, at 95%, the FNN marginally outperformed the CNN at 93%. Hence, this research underlines the probable capability of deep learning techniques in improving the detection of osteoporosis and optimizing diagnostic tools in order to achieve better patient outcomes.
Advancements in Ship Detection: Comparative Analysis of Optical and Hyperspectral Sensors
Oct 11, 2024

Abstract:In marine surveillance, applications span military and civilian domains, including ship detection, marine traffic control, and disaster management. Optical and hyperspectral satellites are key for this purpose. This paper focuses on ship detection and classification techniques, particularly comparing optical and hyperspectral remote sensing approaches. It presents a comprehensive analysis of these technologies, covering feature extraction, methodologies, and their suitability for different missions. The study highlights the importance of selecting the right sensor aligned with mission objectives and conditions, aiming to improve detection accuracy through integrated strategies. The paper examines the strengths and limitations of both technologies in various maritime applications, enhancing understanding of their usability in different operational scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge