Analysing Osteoporosis Detection: A Comparative Study of CNN and FNN
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2024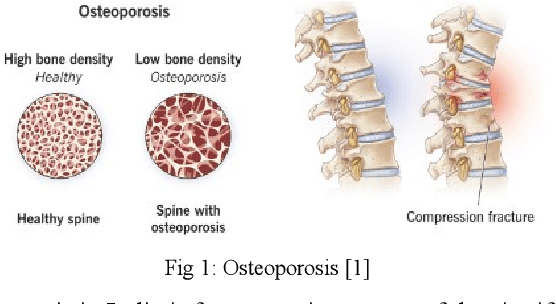
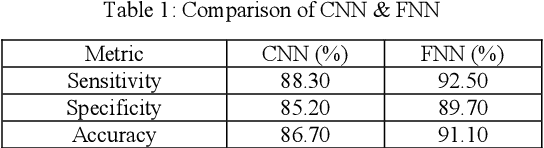
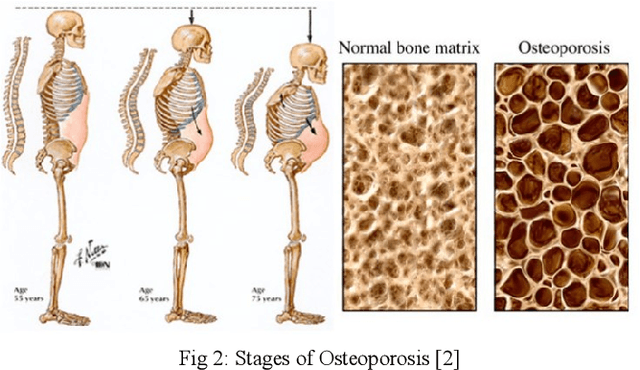
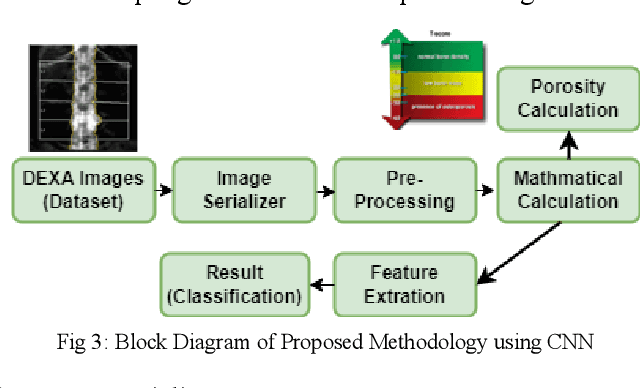
Osteoporosis causes progressive loss of bone density and strength, causing a more elevated risk of fracture than in normal healthy bones. It is estimated that some 1 in 3 women and 1 in 5 men over the age of 50 will experience osteoporotic fractures, which poses osteoporosis as an important public health problem worldwide. The basis of diagnosis is based on Bone Mineral Density (BMD) tests, with Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) being the most common. A T-score of -2.5 or lower defines osteoporosis. This paper focuses on the application of medical imaging analytics towards the detection of osteoporosis by conducting a comparative study of the efficiency of CNN and FNN in DEXA image analytics. Both models are very promising, although, at 95%, the FNN marginally outperformed the CNN at 93%. Hence, this research underlines the probable capability of deep learning techniques in improving the detection of osteoporosis and optimizing diagnostic tools in order to achieve better patient outcomes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge