Akira Kitamura M. S. in IT
A Computer-Aided Diagnosis System Using Artificial Intelligence for Hip Fractures Significantly Improves the Diagnostic Rate of Residents. -Multi-Institutional Joint Development Research-
Apr 07, 2020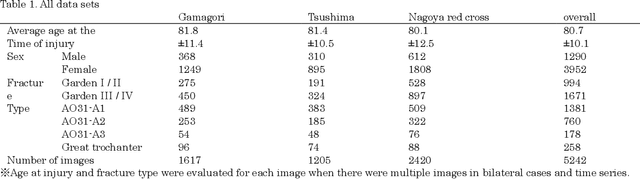
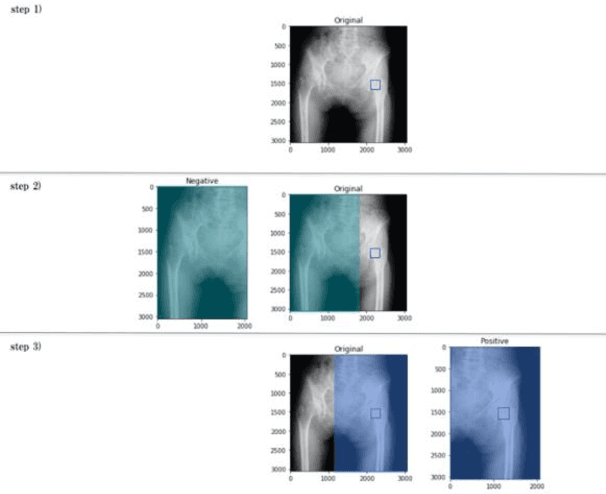
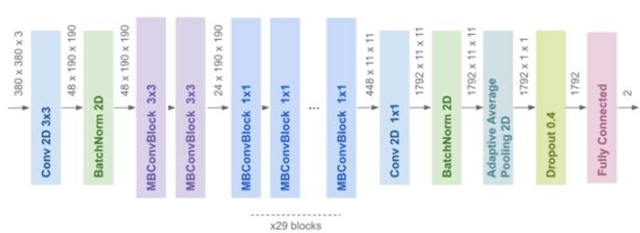
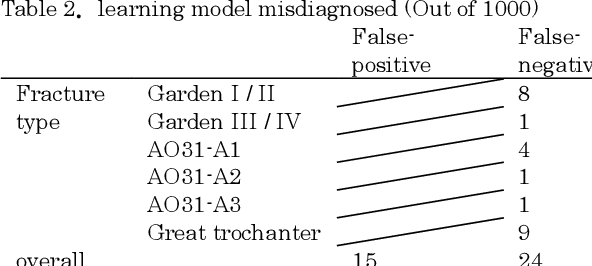
Abstract:[Objective] To develop a CAD system for hip fracture for plain frontal hip X-ray by CNN trained on a large dataset collected at multiple institutions. And, the possibility of the diagnosis rate improvement of the proximal femoral fracture by the resident using this CAD system as an aid of the diagnosis. [Materials and methods] In total, 4851 cases of hip fracture patients who visited each institution between 2009 and 2019 were included. 5242 plain pelvic X-rays were extracted from a DICOM server, and a total of 10484 images(5242 with fracture side and 5242 without fracture side) were used for machine learning. A CNN approach was used. We used the EffectiventNet-B4 framework with Pytorch 1.3 and Fast.ai. In the final evaluation, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, F-value, and AUC were evaluated. Grad-CAM was used to conceptualize the basis of the diagnosis by the CAD system. For 31 residents and 4 orthopedic surgeons, the image diagnosis test was carried out for 600 photographs of hip fracture randomly extracted from test image data set. And, diagnosis rate in the situation with/without the diagnosis support by the CAD system were evaluated respectively. [Results] The diagnostic accuracy of the learning model was 96.1%, sensitivity 95.2%, specificity 96.9%, F value 0.961, and AUC 0.99. Grad-CAM was used to show the most accurate diagnosis. In the image diagnosis test, the resident acquired the diagnostic ability equivalent to that of the orthopedic surgeon by using the diagnostic aid of the CAD system. [Conclusions] The CAD system using AI for the hip fracture which we developed could offer the diagnosis basis, and it became an image diagnosis tool with the high diagnosis accuracy. And, the possibility of contributing to the diagnosis rate improvement was considered in the field of actual clinical environment such as emergency room.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge