Ainara Garcia
Implementing Recycling Methods for Linear Systems in Python with an Application to Multiple Objective Optimization
Feb 25, 2024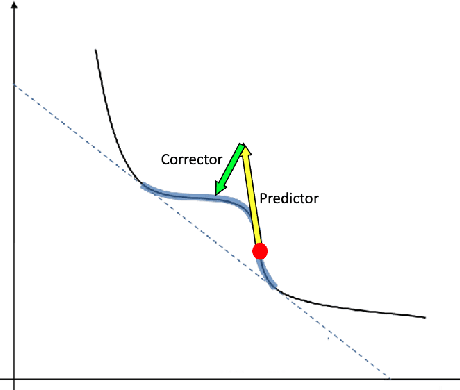
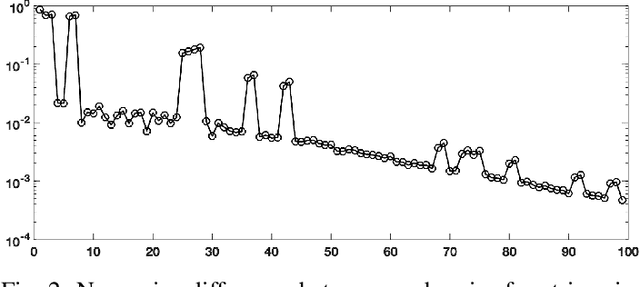
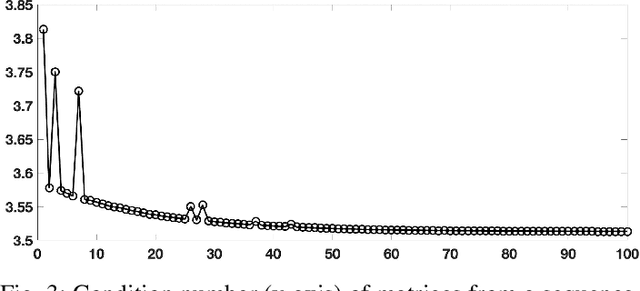
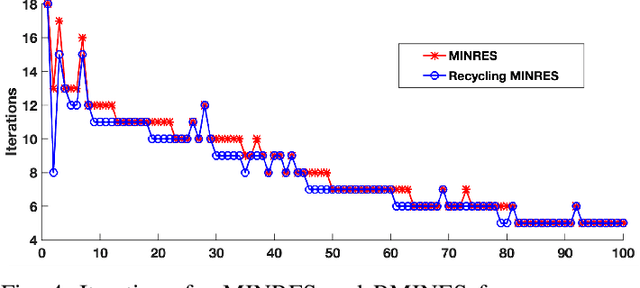
Abstract:Sequences of linear systems arise in the predictor-corrector method when computing the Pareto front for multi-objective optimization. Rather than discarding information generated when solving one system, it may be advantageous to recycle information for subsequent systems. To accomplish this, we seek to reduce the overall cost of computation when solving linear systems using common recycling methods. In this work, we assessed the performance of recycling minimum residual (RMINRES) method along with a map between coefficient matrices. For these methods to be fully integrated into the software used in Enouen et al. (2022), there must be working version of each in both Python and PyTorch. Herein, we discuss the challenges we encountered and solutions undertaken (and some ongoing) when computing efficient Python implementations of these recycling strategies. The goal of this project was to implement RMINRES in Python and PyTorch and add it to the established Pareto front code to reduce computational cost. Additionally, we wanted to implement the sparse approximate maps code in Python and PyTorch, so that it can be parallelized in future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge