Ahmed Mohamed Hussain
Attention in Motion: Secure Platooning via Transformer-based Misbehavior Detection
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Vehicular platooning promises transformative improvements in transportation efficiency and safety through the coordination of multi-vehicle formations enabled by Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication. However, the distributed nature of platoon coordination creates security vulnerabilities, allowing authenticated vehicles to inject falsified kinematic data, compromise operational stability, and pose a threat to passenger safety. Traditional misbehaviour detection approaches, which rely on plausibility checks and statistical methods, suffer from high False Positive (FP) rates and cannot capture the complex temporal dependencies inherent in multi-vehicle coordination dynamics. We present Attention In Motion (AIMformer), a transformer-based framework specifically tailored for real-time misbehaviour detection in vehicular platoons with edge deployment capabilities. AIMformer leverages multi-head self-attention mechanisms to simultaneously capture intra-vehicle temporal dynamics and inter-vehicle spatial correlations. It incorporates global positional encoding with vehicle-specific temporal offsets to handle join/exit maneuvers. We propose a Precision-Focused Binary Cross-Entropy (PFBCE) loss function that penalizes FPs to meet the requirements of safety-critical vehicular systems. Extensive evaluation across 4 platoon controllers, multiple attack vectors, and diverse mobility scenarios demonstrates superior performance ($\geq$ 0.93) compared to state-of-the-art baseline architectures. A comprehensive deployment analysis utilizing TensorFlow Lite (TFLite), Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX), and TensorRT achieves sub-millisecond inference latency, making it suitable for real-time operation on resource-constrained edge platforms. Hence, validating AIMformer is viable for both in-vehicle and roadside infrastructure deployment.
AttentionGuard: Transformer-based Misbehavior Detection for Secure Vehicular Platoons
May 15, 2025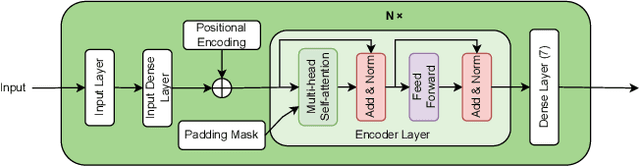


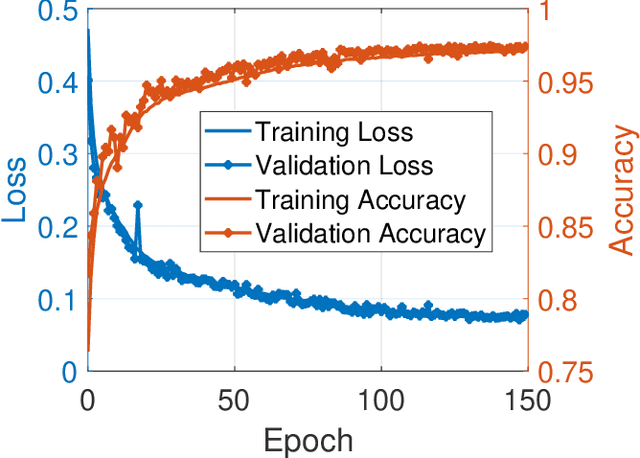
Abstract:Vehicle platooning, with vehicles traveling in close formation coordinated through Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communications, offers significant benefits in fuel efficiency and road utilization. However, it is vulnerable to sophisticated falsification attacks by authenticated insiders that can destabilize the formation and potentially cause catastrophic collisions. This paper addresses this challenge: misbehavior detection in vehicle platooning systems. We present AttentionGuard, a transformer-based framework for misbehavior detection that leverages the self-attention mechanism to identify anomalous patterns in mobility data. Our proposal employs a multi-head transformer-encoder to process sequential kinematic information, enabling effective differentiation between normal mobility patterns and falsification attacks across diverse platooning scenarios, including steady-state (no-maneuver) operation, join, and exit maneuvers. Our evaluation uses an extensive simulation dataset featuring various attack vectors (constant, gradual, and combined falsifications) and operational parameters (controller types, vehicle speeds, and attacker positions). Experimental results demonstrate that AttentionGuard achieves up to 0.95 F1-score in attack detection, with robust performance maintained during complex maneuvers. Notably, our system performs effectively with minimal latency (100ms decision intervals), making it suitable for real-time transportation safety applications. Comparative analysis reveals superior detection capabilities and establishes the transformer-encoder as a promising approach for securing Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems (C-ITS) against sophisticated insider threats.
LLMs Have Rhythm: Fingerprinting Large Language Models Using Inter-Token Times and Network Traffic Analysis
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) become increasingly integrated into many technological ecosystems across various domains and industries, identifying which model is deployed or being interacted with is critical for the security and trustworthiness of the systems. Current verification methods typically rely on analyzing the generated output to determine the source model. However, these techniques are susceptible to adversarial attacks, operate in a post-hoc manner, and may require access to the model weights to inject a verifiable fingerprint. In this paper, we propose a novel passive and non-invasive fingerprinting technique that operates in real-time and remains effective even under encrypted network traffic conditions. Our method leverages the intrinsic autoregressive generation nature of language models, which generate text one token at a time based on all previously generated tokens, creating a unique temporal pattern like a rhythm or heartbeat that persists even when the output is streamed over a network. We find that measuring the Inter-Token Times (ITTs)-time intervals between consecutive tokens-can identify different language models with high accuracy. We develop a Deep Learning (DL) pipeline to capture these timing patterns using network traffic analysis and evaluate it on 16 Small Language Models (SLMs) and 10 proprietary LLMs across different deployment scenarios, including local host machine (GPU/CPU), Local Area Network (LAN), Remote Network, and Virtual Private Network (VPN). The experimental results confirm that our proposed technique is effective and maintains high accuracy even when tested in different network conditions. This work opens a new avenue for model identification in real-world scenarios and contributes to more secure and trustworthy language model deployment.
CySecBench: Generative AI-based CyberSecurity-focused Prompt Dataset for Benchmarking Large Language Models
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Numerous studies have investigated methods for jailbreaking Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate harmful content. Typically, these methods are evaluated using datasets of malicious prompts designed to bypass security policies established by LLM providers. However, the generally broad scope and open-ended nature of existing datasets can complicate the assessment of jailbreaking effectiveness, particularly in specific domains, notably cybersecurity. To address this issue, we present and publicly release CySecBench, a comprehensive dataset containing 12662 prompts specifically designed to evaluate jailbreaking techniques in the cybersecurity domain. The dataset is organized into 10 distinct attack-type categories, featuring close-ended prompts to enable a more consistent and accurate assessment of jailbreaking attempts. Furthermore, we detail our methodology for dataset generation and filtration, which can be adapted to create similar datasets in other domains. To demonstrate the utility of CySecBench, we propose and evaluate a jailbreaking approach based on prompt obfuscation. Our experimental results show that this method successfully elicits harmful content from commercial black-box LLMs, achieving Success Rates (SRs) of 65% with ChatGPT and 88% with Gemini; in contrast, Claude demonstrated greater resilience with a jailbreaking SR of 17%. Compared to existing benchmark approaches, our method shows superior performance, highlighting the value of domain-specific evaluation datasets for assessing LLM security measures. Moreover, when evaluated using prompts from a widely used dataset (i.e., AdvBench), it achieved an SR of 78.5%, higher than the state-of-the-art methods.
Edge AI-based Radio Frequency Fingerprinting for IoT Networks
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:The deployment of the Internet of Things (IoT) in smart cities and critical infrastructure has enhanced connectivity and real-time data exchange but introduced significant security challenges. While effective, cryptography can often be resource-intensive for small-footprint resource-constrained (i.e., IoT) devices. Radio Frequency Fingerprinting (RFF) offers a promising authentication alternative by using unique RF signal characteristics for device identification at the Physical (PHY)-layer, without resorting to cryptographic solutions. The challenge is two-fold: how to deploy such RFF in a large scale and for resource-constrained environments. Edge computing, processing data closer to its source, i.e., the wireless device, enables faster decision-making, reducing reliance on centralized cloud servers. Considering a modest edge device, we introduce two truly lightweight Edge AI-based RFF schemes tailored for resource-constrained devices. We implement two Deep Learning models, namely a Convolution Neural Network and a Transformer-Encoder, to extract complex features from the IQ samples, forming device-specific RF fingerprints. We convert the models to TensorFlow Lite and evaluate them on a Raspberry Pi, demonstrating the practicality of Edge deployment. Evaluations demonstrate the Transformer-Encoder outperforms the CNN in identifying unique transmitter features, achieving high accuracy (> 0.95) and ROC-AUC scores (> 0.90) while maintaining a compact model size of 73KB, appropriate for resource-constrained devices.
The Dark Side of IoT: Attacks and Countermeasures to Identification of Smart Home Devices and Services
Sep 20, 2020



Abstract:We present a new machine learning-based attack that exploits network patterns to detect the presence of smart IoT devices and running services in the WiFi radio spectrum. We perform an extensive measurement campaign of data collection, and we build up a model describing the traffic patterns characterizing three popular IoT smart home devices, i.e., Google Nest, Google Chromecast, Amazon Echo, and Amazon Echo Dot. We prove that it is possible to detect and identify with overwhelming probability their presence and the services running by the aforementioned devices in a crowded WiFi scenario. This work proves that standard encryption techniques alone are not sufficient to protect the privacy of the end-user, since the network traffic itself exposes the presence of both the device and the associated service. While more work is required to prevent non-trusted third parties to detect and identify the user's devices, we introduce "Eclipse", a technique to mitigate these types of attacks, which reshapes the traffic making the identification of the devices and the associated services similar to the random classification baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge