Ahmed Hemani
Department of Electronics and Embedded Systems, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden
'1'-bit Count-based Sorting Unit to Reduce Link Power in DNN Accelerators
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Interconnect power consumption remains a bottleneck in Deep Neural Network (DNN) accelerators. While ordering data based on '1'-bit counts can mitigate this via reduced switching activity, practical hardware sorting implementations remain underexplored. This work proposes the hardware implementation of a comparison-free sorting unit optimized for Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). By leveraging approximate computing to group population counts into coarse-grained buckets, our design achieves hardware area reductions while preserving the link power benefits of data reordering. Our approximate sorting unit achieves up to 35.4% area reduction while maintaining 19.50\% BT reduction compared to 20.42% of precise implementation.
Late Breaking Results: Quamba-SE: Soft-edge Quantizer for Activations in State Space Models
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:We propose Quamba-SE, a soft-edge quantizer for State Space Model (SSM) activation quantization. Unlike existing methods, using standard INT8 operation, Quamba-SE employs three adaptive scales: high-precision for small values, standard scale for normal values, and low-precision for outliers. This preserves outlier information instead of hard clipping, while maintaining precision for other values. We evaluate on Mamba- 130M across 6 zero-shot benchmarks. Results show that Quamba- SE consistently outperforms Quamba, achieving up to +2.68% on individual benchmarks and up to +0.83% improvement in the average accuracy of 6 datasets.
Multi-objective Recurrent Neural Networks Optimization for the Edge -- a Quantization-based Approach
Aug 02, 2021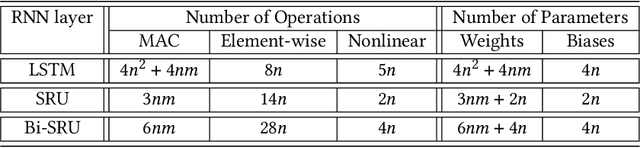

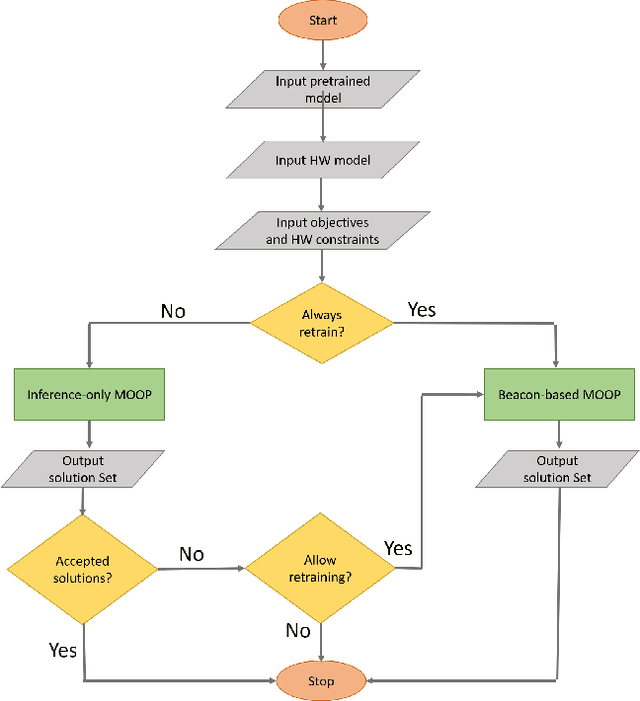
Abstract:The compression of deep learning models is of fundamental importance in deploying such models to edge devices. Incorporating hardware model and application constraints during compression maximizes the benefits but makes it specifically designed for one case. Therefore, the compression needs to be automated. Searching for the optimal compression method parameters is considered an optimization problem. This article introduces a Multi-Objective Hardware-Aware Quantization (MOHAQ) method, which considers both hardware efficiency and inference error as objectives for mixed-precision quantization. The proposed method makes the evaluation of candidate solutions in a large search space feasible by relying on two steps. First, post-training quantization is applied for fast solution evaluation. Second, we propose a search technique named "beacon-based search" to retrain selected solutions only in the search space and use them as beacons to know the effect of retraining on other solutions. To evaluate the optimization potential, we chose a speech recognition model using the TIMIT dataset. The model is based on Simple Recurrent Unit (SRU) due to its considerable speedup over other recurrent units. We applied our method to run on two platforms: SiLago and Bitfusion. Experimental evaluations showed that SRU can be compressed up to 8x by post-training quantization without any significant increase in the error and up to 12x with only a 1.5 percentage point increase in error. On SiLago, the inference-only search found solutions that achieve 80\% and 64\% of the maximum possible speedup and energy saving, respectively, with a 0.5 percentage point increase in the error. On Bitfusion, with a constraint of a small SRAM size, beacon-based search reduced the error gain of inference-only search by 4 percentage points and increased the possible reached speedup to be 47x compared to the Bitfusion baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge