Ahmad Droby
Unsupervised learning of text line segmentation by differentiating coarse patterns
May 21, 2021

Abstract:Despite recent advances in the field of supervised deep learning for text line segmentation, unsupervised deep learning solutions are beginning to gain popularity. In this paper, we present an unsupervised deep learning method that embeds document image patches to a compact Euclidean space where distances correspond to a coarse text line pattern similarity. Once this space has been produced, text line segmentation can be easily implemented using standard techniques with the embedded feature vectors. To train the model, we extract random pairs of document image patches with the assumption that neighbour patches contain a similar coarse trend of text lines, whereas if one of them is rotated, they contain different coarse trends of text lines. Doing well on this task requires the model to learn to recognize the text lines and their salient parts. The benefit of our approach is zero manual labelling effort. We evaluate the method qualitatively and quantitatively on several variants of text line segmentation datasets to demonstrate its effectivity.
Text Line Segmentation for Challenging Handwritten Document Images Using Fully Convolutional Network
Jan 20, 2021

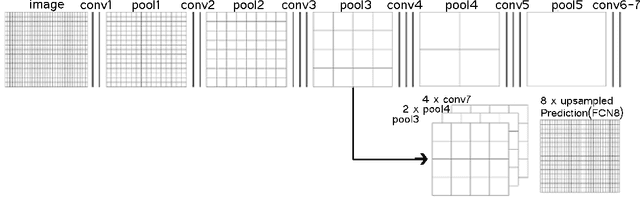

Abstract:This paper presents a method for text line segmentation of challenging historical manuscript images. These manuscript images contain narrow interline spaces with touching components, interpenetrating vowel signs and inconsistent font types and sizes. In addition, they contain curved, multi-skewed and multi-directed side note lines within a complex page layout. Therefore, bounding polygon labeling would be very difficult and time consuming. Instead we rely on line masks that connect the components on the same text line. Then these line masks are predicted using a Fully Convolutional Network (FCN). In the literature, FCN has been successfully used for text line segmentation of regular handwritten document images. The present paper shows that FCN is useful with challenging manuscript images as well. Using a new evaluation metric that is sensitive to over segmentation as well as under segmentation, testing results on a publicly available challenging handwritten dataset are comparable with the results of a previous work on the same dataset.
Unsupervised Deep Learning for Handwritten Page Segmentation
Jan 19, 2021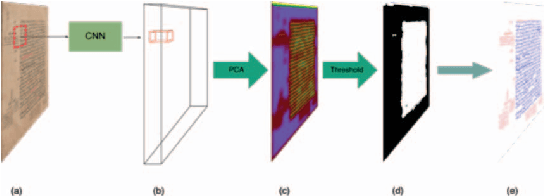



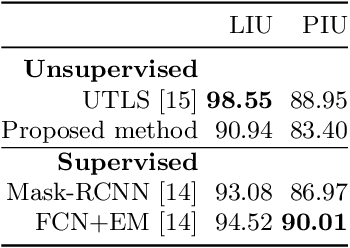
Abstract:Segmenting handwritten document images into regions with homogeneous patterns is an important pre-processing step for many document images analysis tasks. Hand-labeling data to train a deep learning model for layout analysis requires significant human effort. In this paper, we present an unsupervised deep learning method for page segmentation, which revokes the need for annotated images. A siamese neural network is trained to differentiate between patches using their measurable properties such as number of foreground pixels, and average component height and width. The network is trained that spatially nearby patches are similar. The network's learned features are used for page segmentation, where patches are classified as main and side text based on the extracted features. We tested the method on a dataset of handwritten document images with quite complex layouts. Our experiments show that the proposed unsupervised method is as effective as typical supervised methods.
Text line extraction using fully convolutional network and energy minimization
Jan 18, 2021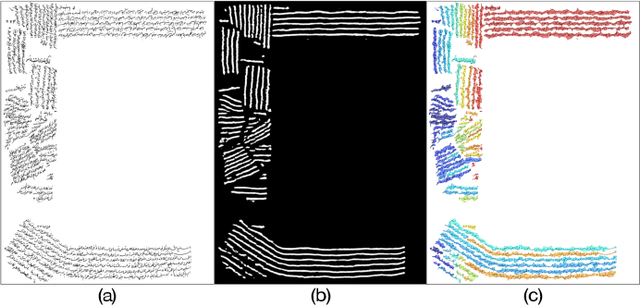



Abstract:Text lines are important parts of handwritten document images and easier to analyze by further applications. Despite recent progress in text line detection, text line extraction from a handwritten document remains an unsolved task. This paper proposes to use a fully convolutional network for text line detection and energy minimization for text line extraction. Detected text lines are represented by blob lines that strike through the text lines. These blob lines assist an energy function for text line extraction. The detection stage can locate arbitrarily oriented text lines. Furthermore, the extraction stage is capable of finding out the pixels of text lines with various heights and interline proximity independent of their orientations. Besides, it can finely split the touching and overlapping text lines without an orientation assumption. We evaluate the proposed method on VML-AHTE, VML-MOC, and Diva-HisDB datasets. The VML-AHTE dataset contains overlapping, touching and close text lines with rich diacritics. The VML-MOC dataset is very challenging by its multiply oriented and skewed text lines. The Diva-HisDB dataset exhibits distinct text line heights and touching text lines. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the method despite various types of challenges, yet using the same parameters in all the experiments.
ContourCNN: convolutional neural network for contour data classification
Sep 30, 2020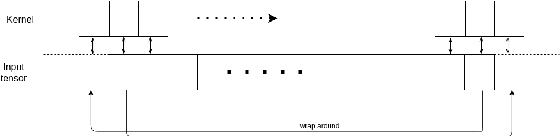
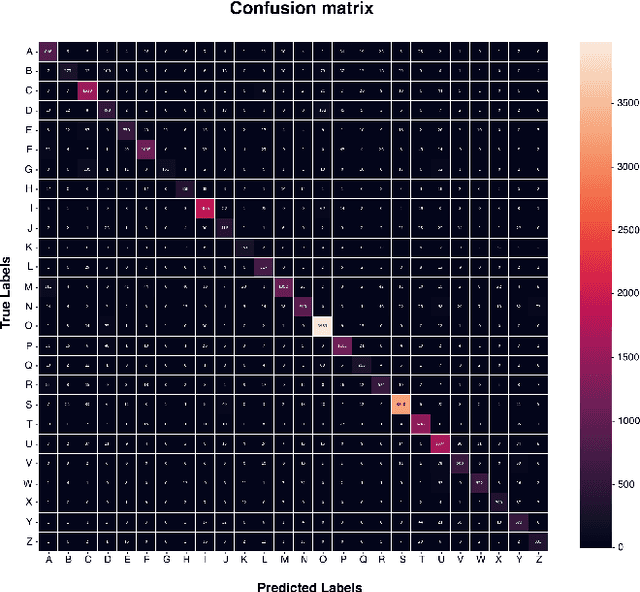
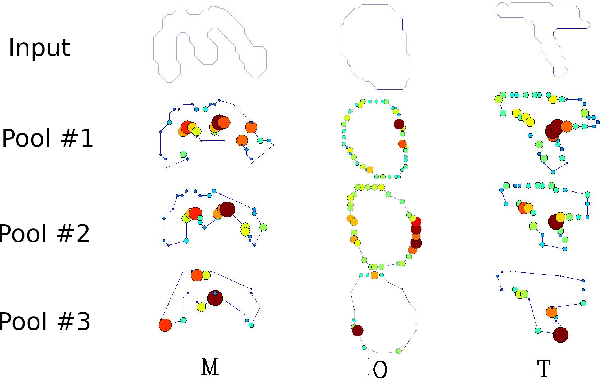

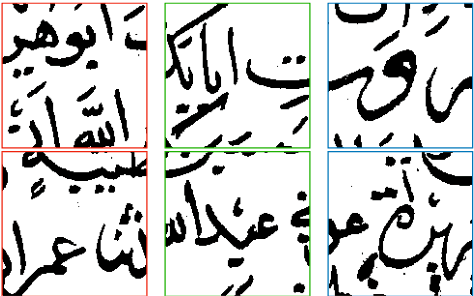
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel Convolutional Neural Network model for contour data analysis (ContourCNN) and shape classification. A contour is a circular sequence of points representing a closed shape. For handling the cyclical property of the contour representation, we employ circular convolution layers. Contours are often represented sparsely. To address information sparsity, we introduce priority pooling layers that select features based on their magnitudes. Priority pooling layers pool features with low magnitudes while leaving the rest unchanged. We evaluated the proposed model using letters and digits shapes extracted from the EMNIST dataset and obtained a high classification accuracy.
Unsupervised text line segmentation
Mar 19, 2020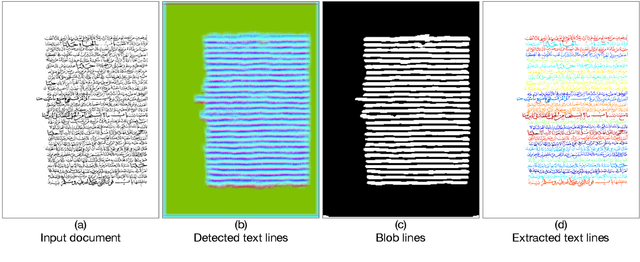

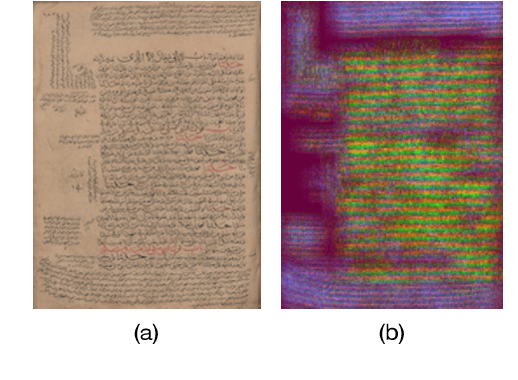
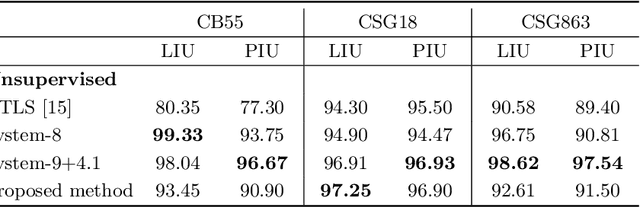
Abstract:We present an unsupervised text line segmentation method that is inspired by the relative variance between text lines and spaces among text lines. Handwritten text line segmentation is important for the efficiency of further processing. A common method is to train a deep learning network for embedding the document image into an image of blob lines that are tracing the text lines. Previous methods learned such embedding in a supervised manner, requiring the annotation of many document images. This paper presents an unsupervised embedding of document image patches without a need for annotations. The main idea is that the number of foreground pixels over the text lines is relatively different from the number of foreground pixels over the spaces among text lines. Generating similar and different pairs relying on this principle definitely leads to outliers. However, as the results show, the outliers do not harm the convergence and the network learns to discriminate the text lines from the spaces between text lines. We experimented with a challenging Arabic handwritten text line segmentation dataset, VML-AHTE, and achieved a superior performance even over the supervised methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge