Afshin Sadeghi
Linking Physicians to Medical Research Results via Knowledge Graph Embeddings and Twitter
Jul 24, 2019



Abstract:Informing professionals about the latest research results in their field is a particularly important task in the field of health care, since any development in this field directly improves the health status of the patients. Meanwhile, social media is an infrastructure that allows public instant sharing of information, thus it has recently become popular in medical applications. In this study, we apply Multi Distance Knowledge Graph Embeddings (MDE) to link physicians and surgeons to the latest medical breakthroughs that are shared as the research results on Twitter. Our study shows that using this method physicians can be informed about the new findings in their field given that they have an account dedicated to their profession.
MDE: Multi Distance Embeddings for Link Prediction in Knowledge Graphs
Jun 10, 2019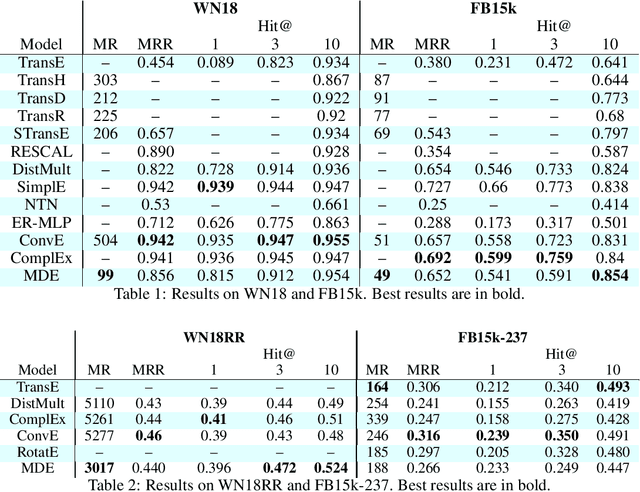
Abstract:Over the past decade, knowledge graphs became popular for capturing structured domain knowledge. Relational learning models enable the prediction of missing links inside knowledge graphs. More specifically, latent distance approaches model the relationships among entities via a distance between latent representations. Translating embedding models (e.g., TransE) are among the most popular latent distance approaches which use one distance function to learn multiple relation patterns. However, they are not capable of capturing symmetric relations. They also force relations with reflexive patterns to become symmetric and transitive. In order to improve distance based embedding, we propose multi-distance embeddings (MDE). Our solution is based on the idea that by learning independent embedding vectors for each entity and relation one can aggregate contrasting distance functions. Benefiting from MDE, we also develop supplementary distances resolving the above-mentioned limitations of TransE. We further propose an extended loss function for distance based embeddings and show that MDE and TransE are fully expressive using this loss function. Furthermore, we obtain a bound on the size of their embeddings for full expressivity. Our empirical results show that MDE significantly improves the translating embeddings and outperforms several state-of-the-art embedding models on benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge