Aditya Prakash Patra
Self-Attention Dense Depth Estimation Network for Unrectified Video Sequences
May 28, 2020
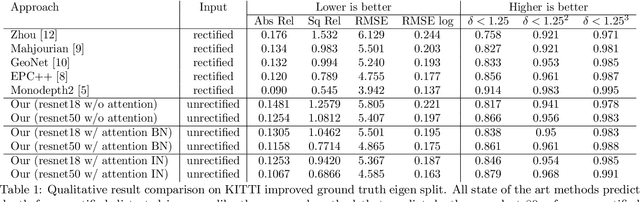
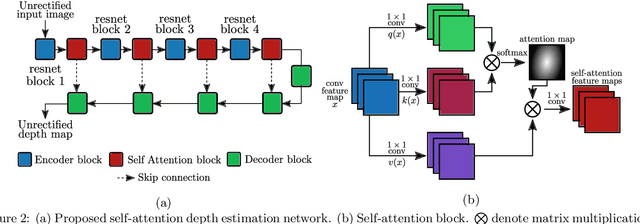
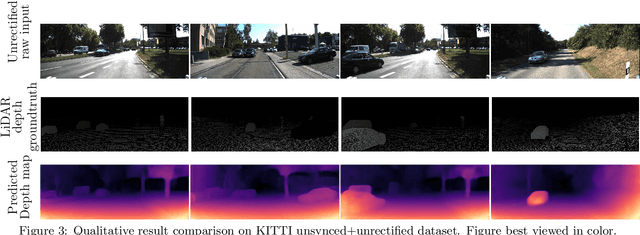
Abstract:The dense depth estimation of a 3D scene has numerous applications, mainly in robotics and surveillance. LiDAR and radar sensors are the hardware solution for real-time depth estimation, but these sensors produce sparse depth maps and are sometimes unreliable. In recent years research aimed at tackling depth estimation using single 2D image has received a lot of attention. The deep learning based self-supervised depth estimation methods from the rectified stereo and monocular video frames have shown promising results. We propose a self-attention based depth and ego-motion network for unrectified images. We also introduce non-differentiable distortion of the camera into the training pipeline. Our approach performs competitively when compared to other established approaches that used rectified images for depth estimation.
Monocular Depth Estimators: Vulnerabilities and Attacks
May 28, 2020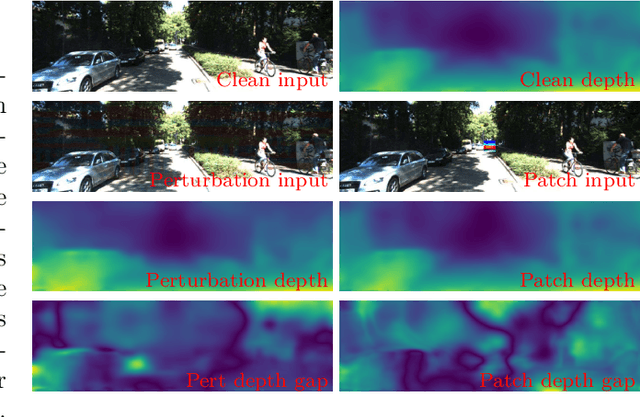
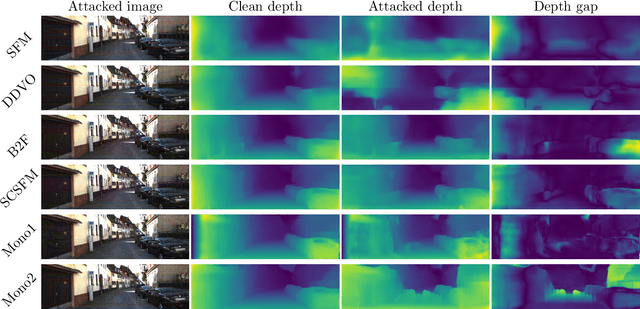

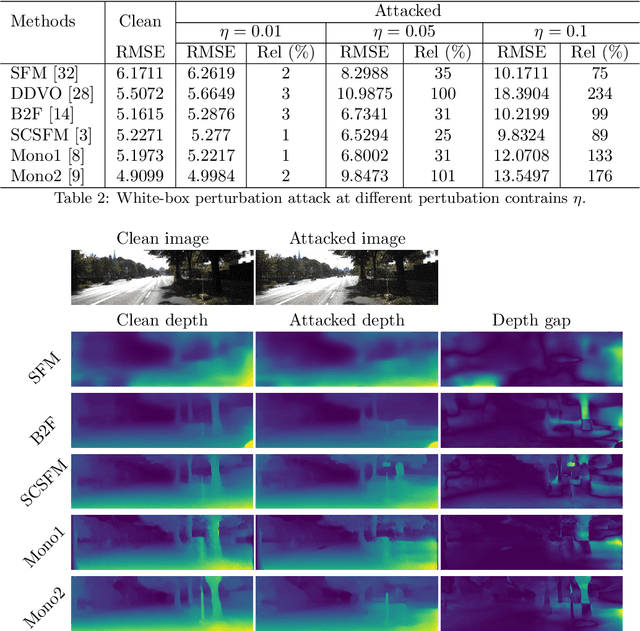
Abstract:Recent advancements of neural networks lead to reliable monocular depth estimation. Monocular depth estimated techniques have the upper hand over traditional depth estimation techniques as it only needs one image during inference. Depth estimation is one of the essential tasks in robotics, and monocular depth estimation has a wide variety of safety-critical applications like in self-driving cars and surgical devices. Thus, the robustness of such techniques is very crucial. It has been shown in recent works that these deep neural networks are highly vulnerable to adversarial samples for tasks like classification, detection and segmentation. These adversarial samples can completely ruin the output of the system, making their credibility in real-time deployment questionable. In this paper, we investigate the robustness of the most state-of-the-art monocular depth estimation networks against adversarial attacks. Our experiments show that tiny perturbations on an image that are invisible to the naked eye (perturbation attack) and corruption less than about 1% of an image (patch attack) can affect the depth estimation drastically. We introduce a novel deep feature annihilation loss that corrupts the hidden feature space representation forcing the decoder of the network to output poor depth maps. The white-box and black-box test compliments the effectiveness of the proposed attack. We also perform adversarial example transferability tests, mainly cross-data transferability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge