Aditya Dutt
Multi-Task Learning with Multi-Annotation Triplet Loss for Improved Object Detection
Apr 10, 2025



Abstract:Triplet loss traditionally relies only on class labels and does not use all available information in multi-task scenarios where multiple types of annotations are available. This paper introduces a Multi-Annotation Triplet Loss (MATL) framework that extends triplet loss by incorporating additional annotations, such as bounding box information, alongside class labels in the loss formulation. By using these complementary annotations, MATL improves multi-task learning for tasks requiring both classification and localization. Experiments on an aerial wildlife imagery dataset demonstrate that MATL outperforms conventional triplet loss in both classification and localization. These findings highlight the benefit of using all available annotations for triplet loss in multi-task learning frameworks.
Mutli-View 3D Reconstruction using Knowledge Distillation
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Large Foundation Models like Dust3r can produce high quality outputs such as pointmaps, camera intrinsics, and depth estimation, given stereo-image pairs as input. However, the application of these outputs on tasks like Visual Localization requires a large amount of inference time and compute resources. To address these limitations, in this paper, we propose the use of a knowledge distillation pipeline, where we aim to build a student-teacher model with Dust3r as the teacher and explore multiple architectures of student models that are trained using the 3D reconstructed points output by Dust3r. Our goal is to build student models that can learn scene-specific representations and output 3D points with replicable performance such as Dust3r. The data set we used to train our models is 12Scenes. We test two main architectures of models: a CNN-based architecture and a Vision Transformer based architecture. For each architecture, we also compare the use of pre-trained models against models built from scratch. We qualitatively compare the reconstructed 3D points output by the student model against Dust3r's and discuss the various features learned by the student model. We also perform ablation studies on the models through hyperparameter tuning. Overall, we observe that the Vision Transformer presents the best performance visually and quantitatively.
Shared Manifold Learning Using a Triplet Network for Multiple Sensor Translation and Fusion with Missing Data
Oct 25, 2022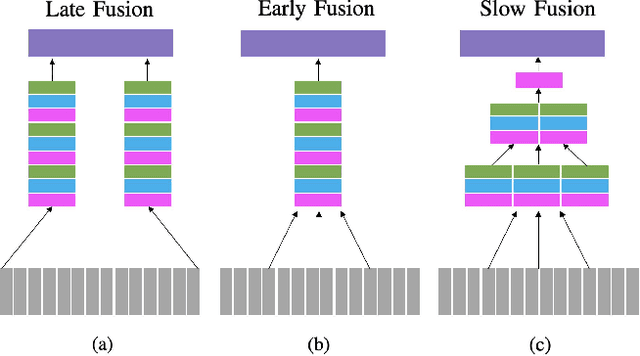
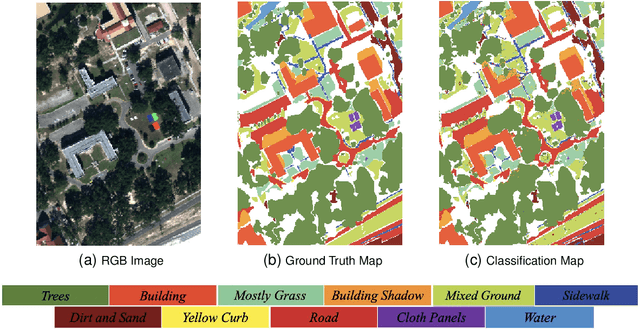
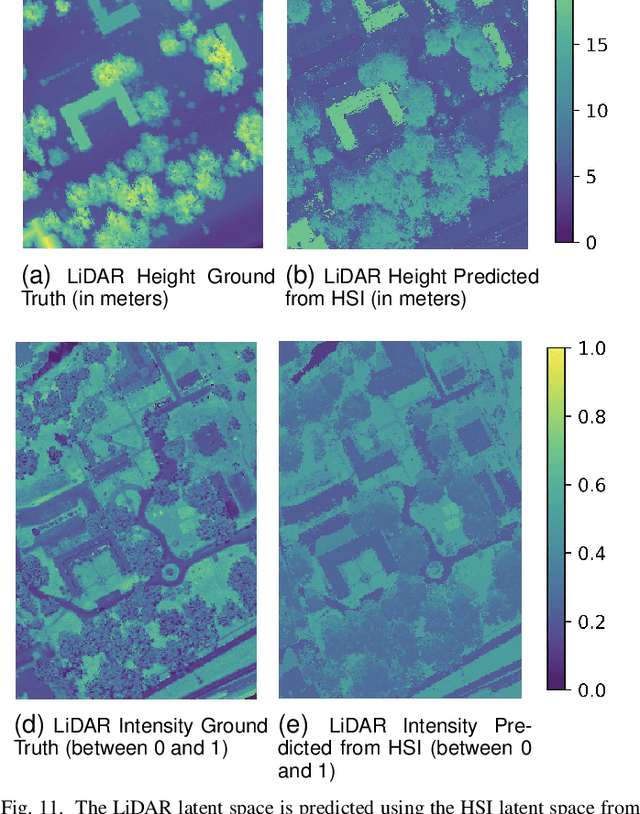
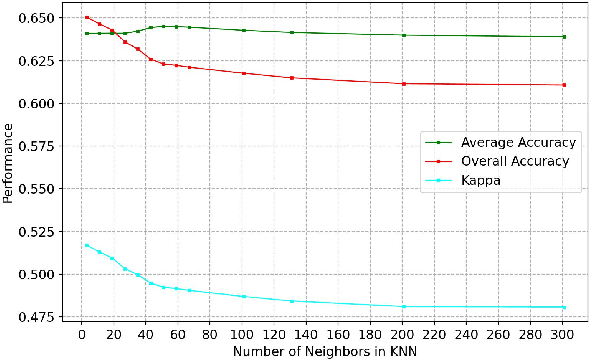
Abstract:Heterogeneous data fusion can enhance the robustness and accuracy of an algorithm on a given task. However, due to the difference in various modalities, aligning the sensors and embedding their information into discriminative and compact representations is challenging. In this paper, we propose a Contrastive learning based MultiModal Alignment Network (CoMMANet) to align data from different sensors into a shared and discriminative manifold where class information is preserved. The proposed architecture uses a multimodal triplet autoencoder to cluster the latent space in such a way that samples of the same classes from each heterogeneous modality are mapped close to each other. Since all the modalities exist in a shared manifold, a unified classification framework is proposed. The resulting latent space representations are fused to perform more robust and accurate classification. In a missing sensor scenario, the latent space of one sensor is easily and efficiently predicted using another sensor's latent space, thereby allowing sensor translation. We conducted extensive experiments on a manually labeled multimodal dataset containing hyperspectral data from AVIRIS-NG and NEON, and LiDAR (light detection and ranging) data from NEON. Lastly, the model is validated on two benchmark datasets: Berlin Dataset (hyperspectral and synthetic aperture radar) and MUUFL Gulfport Dataset (hyperspectral and LiDAR). A comparison made with other methods demonstrates the superiority of this method. We achieved a mean overall accuracy of 94.3% on the MUUFL dataset and the best overall accuracy of 71.26% on the Berlin dataset, which is better than other state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge