Adane Nega Tarekegn
Large Language Model Enhanced Clustering for News Event Detection
Jun 15, 2024Abstract:The news landscape is continuously evolving, with an ever-increasing volume of information from around the world. Automated event detection within this vast data repository is essential for monitoring, identifying, and categorizing significant news occurrences across diverse platforms. This paper presents an event detection framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) combined with clustering analysis to detect news events from the Global Database of Events, Language, and Tone (GDELT). The framework enhances event clustering through both pre-event detection tasks (keyword extraction and text embedding) and post-event detection tasks (event summarization and topic labeling). We also evaluate the impact of various textual embeddings on the quality of clustering outcomes, ensuring robust news categorization. Additionally, we introduce a novel Cluster Stability Assessment Index (CSAI) to assess the validity and robustness of clustering results. CSAI utilizes latent feature vectors to provide a new way of measuring clustering quality. Our experiments indicate that combining LLM embeddings with clustering algorithms yields the best results, demonstrating greater robustness in terms of CSAI scores. Moreover, post-event detection tasks generate meaningful insights, facilitating effective interpretation of event clustering results. Overall, our experimental results indicate that the proposed framework offers valuable insights and could enhance the accuracy and depth of news reporting.
Deep Learning for Multi-Label Learning: A Comprehensive Survey
Jan 29, 2024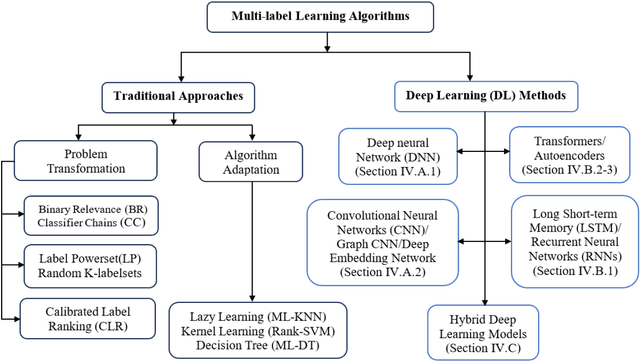
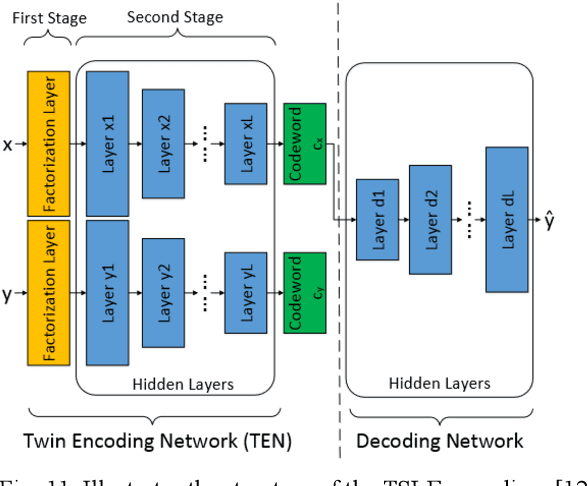
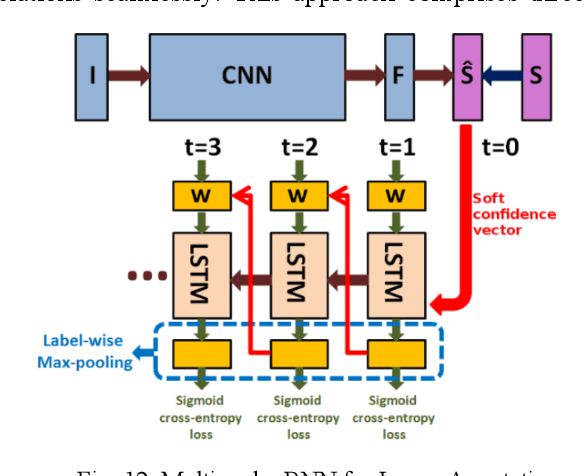
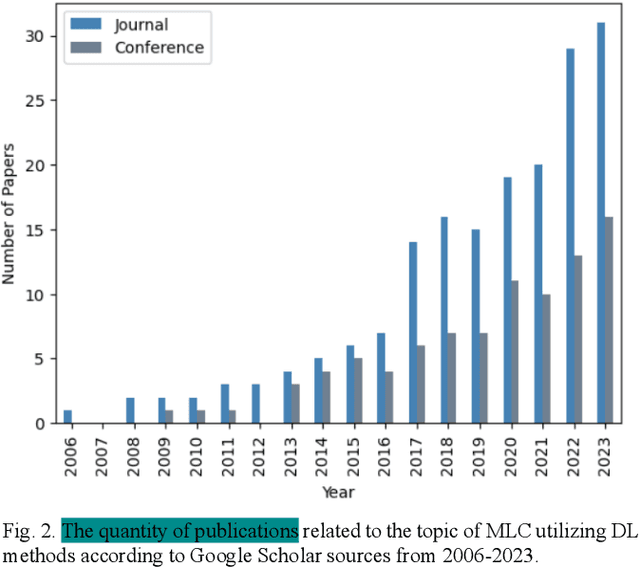
Abstract:Multi-label learning is a rapidly growing research area that aims to predict multiple labels from a single input data point. In the era of big data, tasks involving multi-label classification (MLC) or ranking present significant and intricate challenges, capturing considerable attention in diverse domains. Inherent difficulties in MLC include dealing with high-dimensional data, addressing label correlations, and handling partial labels, for which conventional methods prove ineffective. Recent years have witnessed a notable increase in adopting deep learning (DL) techniques to address these challenges more effectively in MLC. Notably, there is a burgeoning effort to harness the robust learning capabilities of DL for improved modelling of label dependencies and other challenges in MLC. However, it is noteworthy that comprehensive studies specifically dedicated to DL for multi-label learning are limited. Thus, this survey aims to thoroughly review recent progress in DL for multi-label learning, along with a summary of open research problems in MLC. The review consolidates existing research efforts in DL for MLC,including deep neural networks, transformers, autoencoders, and convolutional and recurrent architectures. Finally, the study presents a comparative analysis of the existing methods to provide insightful observations and stimulate future research directions in this domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge