Adam Sutton
On the Learnability of Concepts: With Applications to Comparing Word Embedding Algorithms
Jun 17, 2020



Abstract:Word Embeddings are used widely in multiple Natural Language Processing (NLP) applications. They are coordinates associated with each word in a dictionary, inferred from statistical properties of these words in a large corpus. In this paper we introduce the notion of "concept" as a list of words that have shared semantic content. We use this notion to analyse the learnability of certain concepts, defined as the capability of a classifier to recognise unseen members of a concept after training on a random subset of it. We first use this method to measure the learnability of concepts on pretrained word embeddings. We then develop a statistical analysis of concept learnability, based on hypothesis testing and ROC curves, in order to compare the relative merits of various embedding algorithms using a fixed corpora and hyper parameters. We find that all embedding methods capture the semantic content of those word lists, but fastText performs better than the others.
* 7 Pages. AIAI 2020. 5 equations 6 tables
Biased Embeddings from Wild Data: Measuring, Understanding and Removing
Jun 16, 2018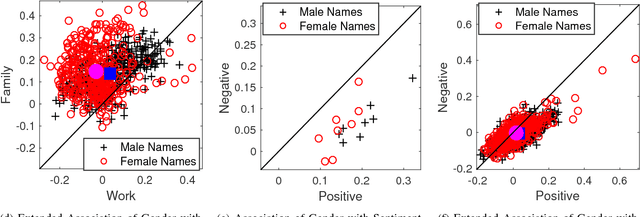

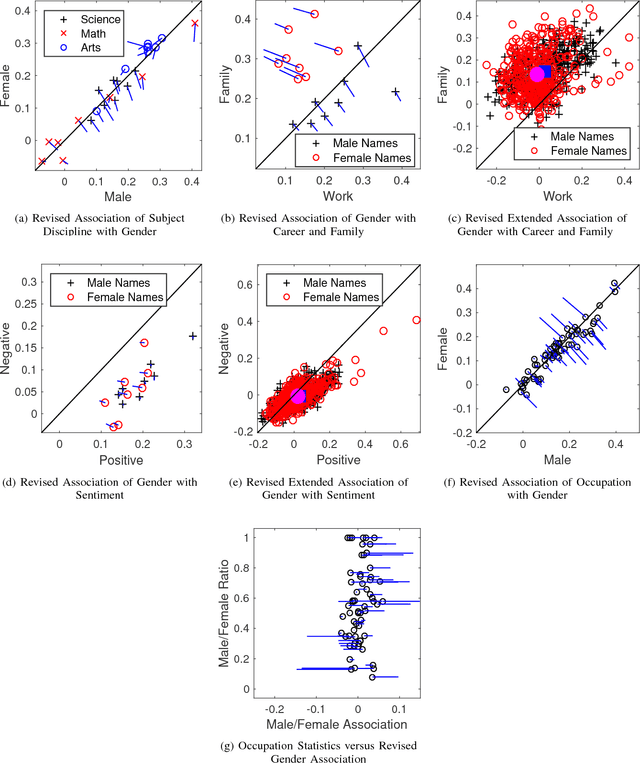

Abstract:Many modern Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems make use of data embeddings, particularly in the domain of Natural Language Processing (NLP). These embeddings are learnt from data that has been gathered "from the wild" and have been found to contain unwanted biases. In this paper we make three contributions towards measuring, understanding and removing this problem. We present a rigorous way to measure some of these biases, based on the use of word lists created for social psychology applications; we observe how gender bias in occupations reflects actual gender bias in the same occupations in the real world; and finally we demonstrate how a simple projection can significantly reduce the effects of embedding bias. All this is part of an ongoing effort to understand how trust can be built into AI systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge