Abhik Banerjee
An IIoT machine model for achieving consistency in product quality in manufacturing plants
Sep 27, 2021



Abstract:Consistency in product quality is of critical importance in manufacturing. However, achieving a target product quality typically involves balancing a large number of manufacturing attributes. Existing manufacturing practices for dealing with such complexity are driven largely based on human knowledge and experience. The prevalence of manual intervention makes it difficult to perfect manufacturing practices, underscoring the need for a data-driven solution. In this paper, we present an Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) machine model which enables effective monitoring and control of plant machinery so as to achieve consistency in product quality. We present algorithms that can provide product quality prediction during production, and provide recommendations for machine control. Subsequently, we perform an experimental evaluation of the proposed solution using real data captured from a food processing plant. We show that the proposed algorithms can be used to predict product quality with a high degree of accuracy, thereby enabling effective production monitoring and control.
Evaluating Sensor Data Quality in Internet ofThings Smart Agriculture Applications
Apr 28, 2021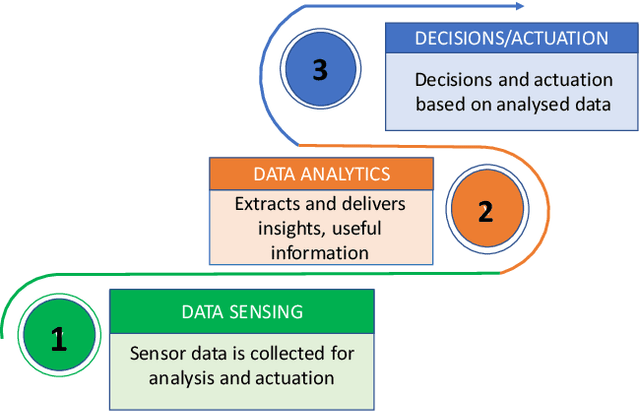
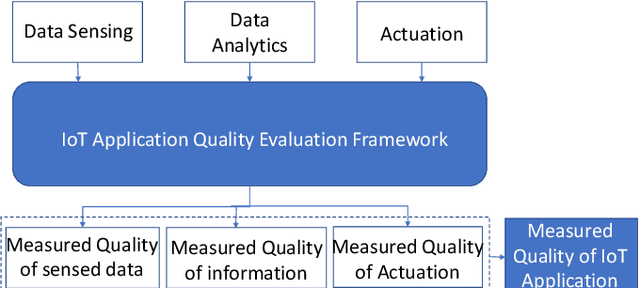
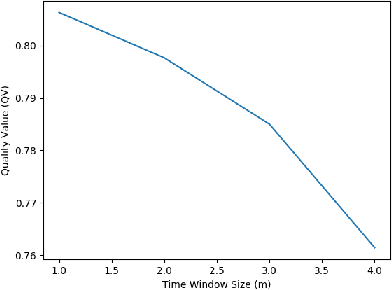
Abstract:The unprecedented growth of Internet of Things (IoT) and its applications in areas such as Smart Agriculture compels the need to devise newer ways for evaluating the quality of such applications. While existing models for application quality focus on the quality experienced by the end-user (captured using likert scale), IoT applications have minimal human involvement and rely on machine to machine communication and analytics to drive decision via actuations. In this paper, we first present a conceptual framework for the evaluation of IoT application quality. Subsequently, we propose, develop and validate via empirical evaluations a novel model for evaluating sensor data quality that is a key component in assessing IoT application quality. We present an implementation of the sensor data quality model and demonstrate how the IoT sensor data quality can be integrated with a Smart Agriculture application. Results of experimental evaluations conducted using data from a real-world testbed concludes the paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge