Abhay Anand Mane
ATM Fraud Detection using Streaming Data Analytics
Mar 08, 2023



Abstract:Gaining the trust and confidence of customers is the essence of the growth and success of financial institutions and organizations. Of late, the financial industry is significantly impacted by numerous instances of fraudulent activities. Further, owing to the generation of large voluminous datasets, it is highly essential that underlying framework is scalable and meet real time needs. To address this issue, in the study, we proposed ATM fraud detection in static and streaming contexts respectively. In the static context, we investigated a parallel and scalable machine learning algorithms for ATM fraud detection that is built on Spark and trained with a variety of machine learning (ML) models including Naive Bayes (NB), Logistic Regression (LR), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Decision Tree (DT), Random Forest (RF), Gradient Boosting Tree (GBT), and Multi-layer perceptron (MLP). We also employed several balancing techniques like Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) and its variants, Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), to address the rarity in the dataset. In addition, we proposed a streaming based ATM fraud detection in the streaming context. Our sliding window based method collects ATM transactions that are performed within a specified time interval and then utilizes to train several ML models, including NB, RF, DT, and K-Nearest Neighbour (KNN). We selected these models based on their less model complexity and quicker response time. In both contexts, RF turned out to be the best model. RF obtained the best mean AUC of 0.975 in the static context and mean AUC of 0.910 in the streaming context. RF is also empirically proven to be statistically significant than the next-best performing models.
Explainable Artificial Intelligence and Causal Inference based ATM Fraud Detection
Nov 19, 2022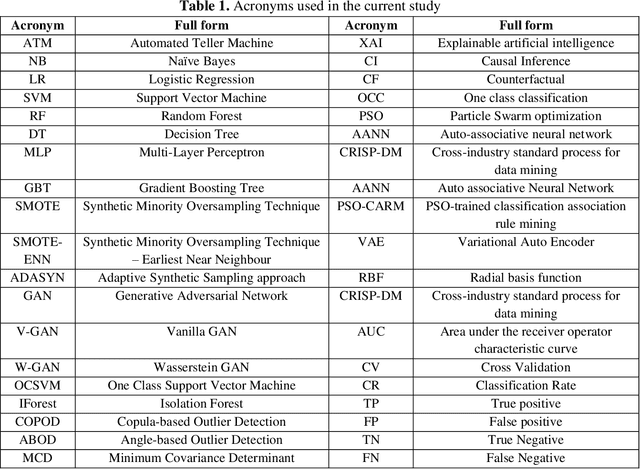


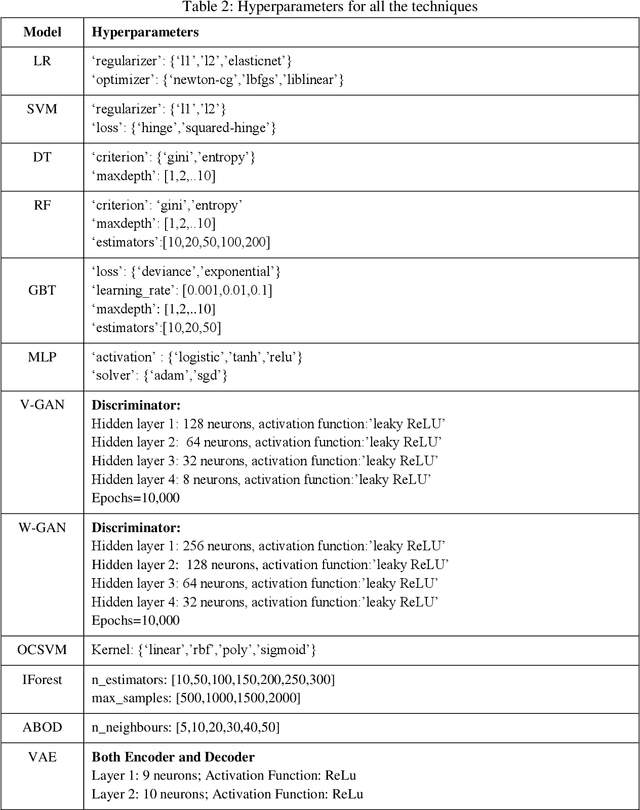
Abstract:Gaining the trust of customers and providing them empathy are very critical in the financial domain. Frequent occurrence of fraudulent activities affects these two factors. Hence, financial organizations and banks must take utmost care to mitigate them. Among them, ATM fraudulent transaction is a common problem faced by banks. There following are the critical challenges involved in fraud datasets: the dataset is highly imbalanced, the fraud pattern is changing, etc. Owing to the rarity of fraudulent activities, Fraud detection can be formulated as either a binary classification problem or One class classification (OCC). In this study, we handled these techniques on an ATM transactions dataset collected from India. In binary classification, we investigated the effectiveness of various over-sampling techniques, such as the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) and its variants, Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), to achieve oversampling. Further, we employed various machine learning techniques viz., Naive Bayes (NB), Logistic Regression (LR), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Decision Tree (DT), Random Forest (RF), Gradient Boosting Tree (GBT), Multi-layer perceptron (MLP). GBT outperformed the rest of the models by achieving 0.963 AUC, and DT stands second with 0.958 AUC. DT is the winner if the complexity and interpretability aspects are considered. Among all the oversampling approaches, SMOTE and its variants were observed to perform better. In OCC, IForest attained 0.959 CR, and OCSVM secured second place with 0.947 CR. Further, we incorporated explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) and causal inference (CI) in the fraud detection framework and studied it through various analyses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge