Abdulmalik Al-Salman
MultiProSE: A Multi-label Arabic Dataset for Propaganda, Sentiment, and Emotion Detection
Feb 12, 2025
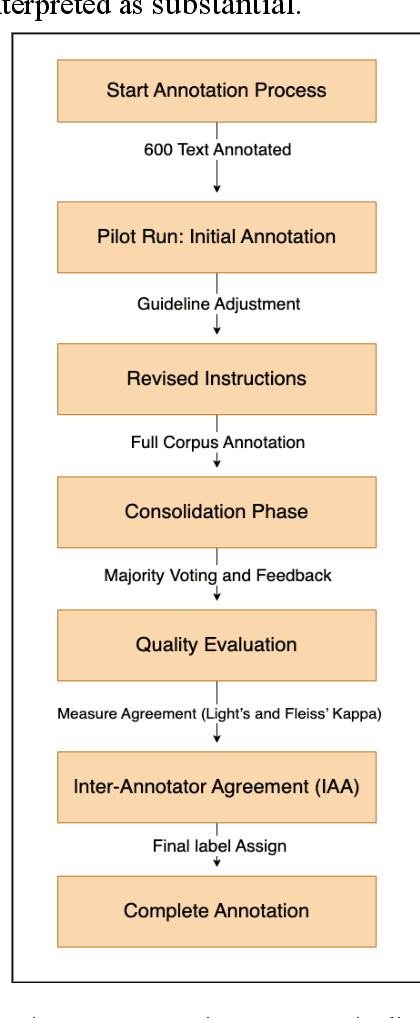
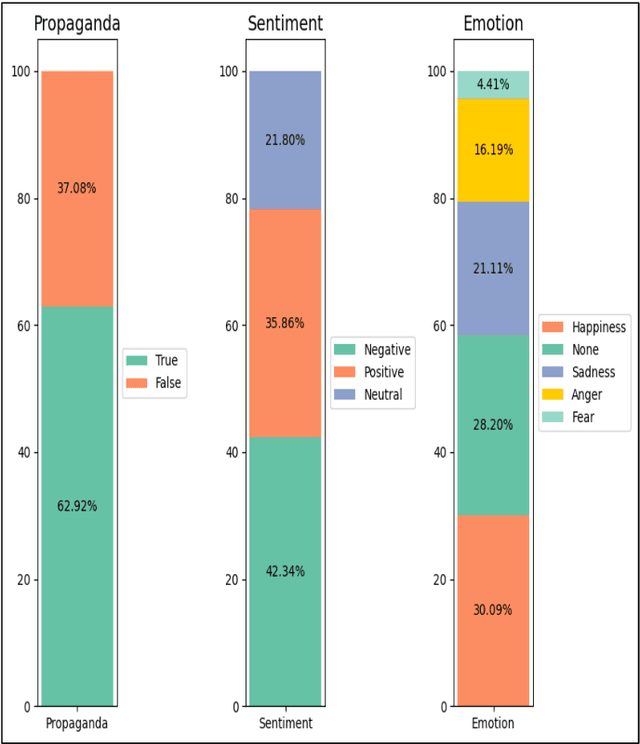
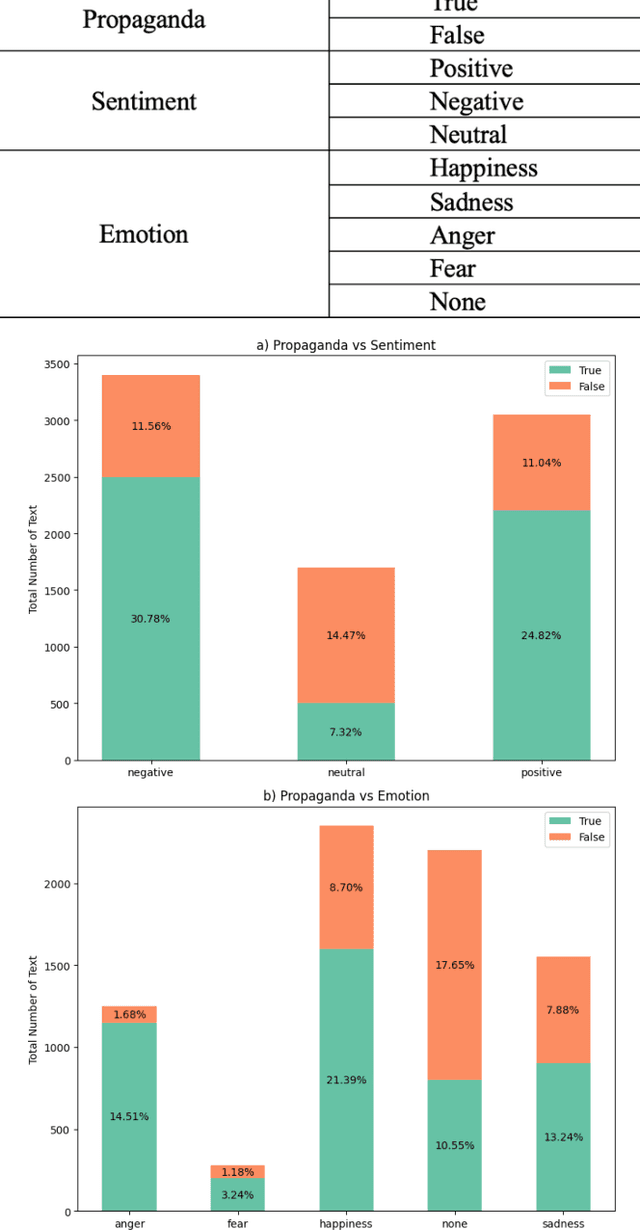
Abstract:Propaganda is a form of persuasion that has been used throughout history with the intention goal of influencing people's opinions through rhetorical and psychological persuasion techniques for determined ends. Although Arabic ranked as the fourth most- used language on the internet, resources for propaganda detection in languages other than English, especially Arabic, remain extremely limited. To address this gap, the first Arabic dataset for Multi-label Propaganda, Sentiment, and Emotion (MultiProSE) has been introduced. MultiProSE is an open-source extension of the existing Arabic propaganda dataset, ArPro, with the addition of sentiment and emotion annotations for each text. This dataset comprises 8,000 annotated news articles, which is the largest propaganda dataset to date. For each task, several baselines have been developed using large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4o-mini, and pre-trained language models (PLMs), including three BERT-based models. The dataset, annotation guidelines, and source code are all publicly released to facilitate future research and development in Arabic language models and contribute to a deeper understanding of how various opinion dimensions interact in news media1.
CLEANANERCorp: Identifying and Correcting Incorrect Labels in the ANERcorp Dataset
Aug 22, 2024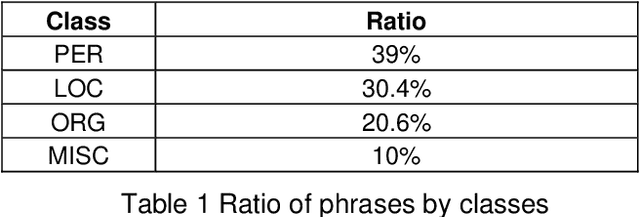
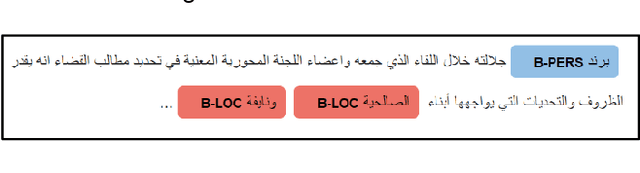
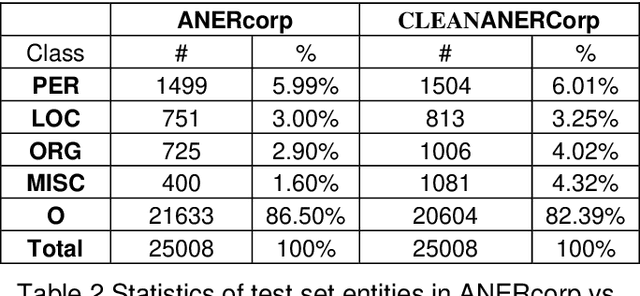
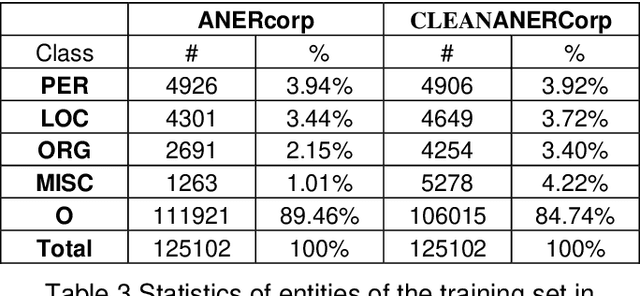
Abstract:Label errors are a common issue in machine learning datasets, particularly for tasks such as Named Entity Recognition. Such label errors might hurt model training, affect evaluation results, and lead to an inaccurate assessment of model performance. In this study, we dived deep into one of the widely adopted Arabic NER benchmark datasets (ANERcorp) and found a significant number of annotation errors, missing labels, and inconsistencies. Therefore, in this study, we conducted empirical research to understand these errors, correct them and propose a cleaner version of the dataset named CLEANANERCorp. CLEANANERCorp will serve the research community as a more accurate and consistent benchmark.
* Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on Open-Source Arabic Corpora and Processing Tools (OSACT) with Shared Tasks on Arabic LLMs Hallucination and Dialect to MSA Machine Translation @ LREC-COLING 2024
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge