Abdelaziz Amara Korba
Fuse and Federate: Enhancing EV Charging Station Security with Multimodal Fusion and Federated Learning
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:The rapid global adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has established electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) as a critical component of smart grid infrastructure. While essential for ensuring reliable energy delivery and accessibility, EVSE systems face significant cybersecurity challenges, including network reconnaissance, backdoor intrusions, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. These emerging threats, driven by the interconnected and autonomous nature of EVSE, require innovative and adaptive security mechanisms that go beyond traditional intrusion detection systems (IDS). Existing approaches, whether network-based or host-based, often fail to detect sophisticated and targeted attacks specifically crafted to exploit new vulnerabilities in EVSE infrastructure. This paper proposes a novel intrusion detection framework that leverages multimodal data sources, including network traffic and kernel events, to identify complex attack patterns. The framework employs a distributed learning approach, enabling collaborative intelligence across EVSE stations while preserving data privacy through federated learning. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework outperforms existing solutions, achieving a detection rate above 98% and a precision rate exceeding 97% in decentralized environments. This solution addresses the evolving challenges of EVSE security, offering a scalable and privacypreserving response to advanced cyber threats
BARTPredict: Empowering IoT Security with LLM-Driven Cyber Threat Prediction
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology in various domains has led to operational advancements, but it has also introduced new vulnerabilities to cybersecurity threats, as evidenced by recent widespread cyberattacks on IoT devices. Intrusion detection systems are often reactive, triggered by specific patterns or anomalies observed within the network. To address this challenge, this work proposes a proactive approach to anticipate and preemptively mitigate malicious activities, aiming to prevent potential damage before it occurs. This paper proposes an innovative intrusion prediction framework empowered by Pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs). The framework incorporates two LLMs: a fine-tuned Bidirectional and AutoRegressive Transformers (BART) model for predicting network traffic and a fine-tuned Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) model for evaluating the predicted traffic. By harnessing the bidirectional capabilities of BART the framework then identifies malicious packets among these predictions. Evaluated using the CICIoT2023 IoT attack dataset, our framework showcases a notable enhancement in predictive performance, attaining an impressive 98% overall accuracy, providing a powerful response to the cybersecurity challenges that confront IoT networks.
Beyond Detection: Leveraging Large Language Models for Cyber Attack Prediction in IoT Networks
Aug 26, 2024Abstract:In recent years, numerous large-scale cyberattacks have exploited Internet of Things (IoT) devices, a phenomenon that is expected to escalate with the continuing proliferation of IoT technology. Despite considerable efforts in attack detection, intrusion detection systems remain mostly reactive, responding to specific patterns or observed anomalies. This work proposes a proactive approach to anticipate and mitigate malicious activities before they cause damage. This paper proposes a novel network intrusion prediction framework that combines Large Language Models (LLMs) with Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) networks. The framework incorporates two LLMs in a feedback loop: a fine-tuned Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) model for predicting network traffic and a fine-tuned Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) for evaluating the predicted traffic. The LSTM classifier model then identifies malicious packets among these predictions. Our framework, evaluated on the CICIoT2023 IoT attack dataset, demonstrates a significant improvement in predictive capabilities, achieving an overall accuracy of 98%, offering a robust solution to IoT cybersecurity challenges.
Anomaly-based Framework for Detecting Power Overloading Cyberattacks in Smart Grid AMI
Jul 03, 2024
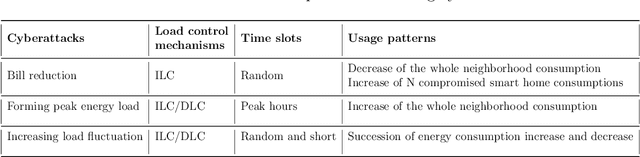
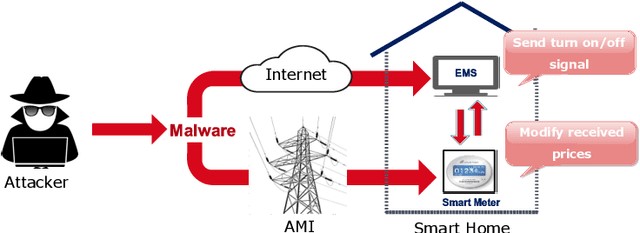

Abstract:The Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) is one of the key components of the smart grid. It provides interactive services for managing billing and electricity consumption, but it also introduces new vectors for cyberattacks. Although, the devastating and severe impact of power overloading cyberattacks on smart grid AMI, few researches in the literature have addressed them. In the present paper, we propose a two-level anomaly detection framework based on regression decision trees. The introduced detection approach leverages the regularity and predictability of energy consumption to build reference consumption patterns for the whole neighborhood and each household within it. Using a reference consumption pattern enables detecting power overloading cyberattacks regardless of the attacker's strategy as they cause a drastic change in the consumption pattern. The continuous two-level monitoring of energy consumption load allows efficient and early detection of cyberattacks. We carried out an extensive experiment on a real-world publicly available energy consumption dataset of 500 customers in Ireland. We extracted, from the raw data, the relevant attributes for training the energy consumption patterns. The evaluation shows that our approach achieves a high detection rate, a low false alarm rate, and superior performances compared to existing solutions.
AntibotV: A Multilevel Behaviour-based Framework for Botnets Detection in Vehicular Networks
Jul 03, 2024Abstract:Connected cars offer safety and efficiency for both individuals and fleets of private vehicles and public transportation companies. However, equipping vehicles with information and communication technologies raises privacy and security concerns, which significantly threaten the user's data and life. Using bot malware, a hacker may compromise a vehicle and control it remotely, for instance, he can disable breaks or start the engine remotely. In this paper, besides in-vehicle attacks existing in the literature, we consider new zeroday bot malware attacks specific to the vehicular context, WSMP-Flood, and Geo-WSMP Flood. Then, we propose AntibotV, a multilevel behaviour-based framework for vehicular botnets detection in vehicular networks. The proposed framework combines two main modules for attack detection, the first one monitors the vehicle's activity at the network level, whereas the second one monitors the in-vehicle activity. The two intrusion detection modules have been trained on a historical network and in-vehicle communication using decision tree algorithms. The experimental results showed that the proposed framework outperforms existing solutions, it achieves a detection rate higher than 97% and a false positive rate lower than 0.14%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge