Anomaly-based Framework for Detecting Power Overloading Cyberattacks in Smart Grid AMI
Paper and Code
Jul 03, 2024
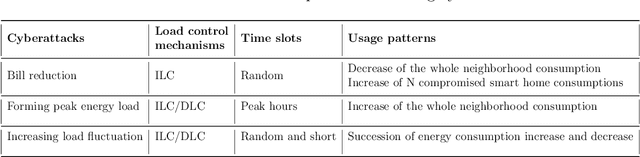
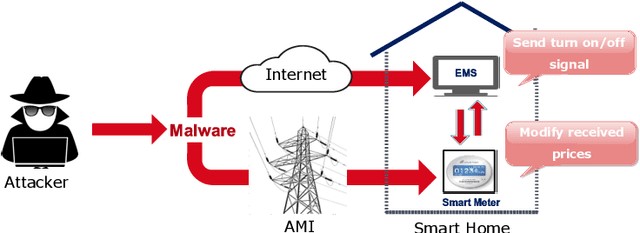

The Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) is one of the key components of the smart grid. It provides interactive services for managing billing and electricity consumption, but it also introduces new vectors for cyberattacks. Although, the devastating and severe impact of power overloading cyberattacks on smart grid AMI, few researches in the literature have addressed them. In the present paper, we propose a two-level anomaly detection framework based on regression decision trees. The introduced detection approach leverages the regularity and predictability of energy consumption to build reference consumption patterns for the whole neighborhood and each household within it. Using a reference consumption pattern enables detecting power overloading cyberattacks regardless of the attacker's strategy as they cause a drastic change in the consumption pattern. The continuous two-level monitoring of energy consumption load allows efficient and early detection of cyberattacks. We carried out an extensive experiment on a real-world publicly available energy consumption dataset of 500 customers in Ireland. We extracted, from the raw data, the relevant attributes for training the energy consumption patterns. The evaluation shows that our approach achieves a high detection rate, a low false alarm rate, and superior performances compared to existing solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge