Aashu Jha
Wideband physical layer cognitive radio with an integrated photonic processor for blind source separation
May 17, 2022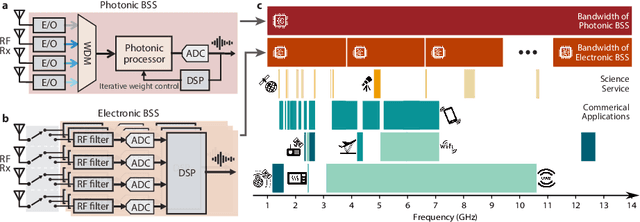
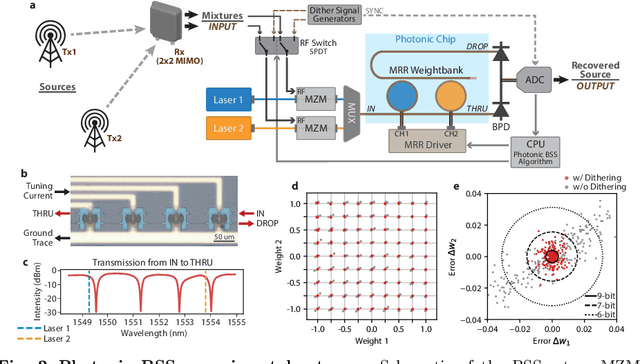
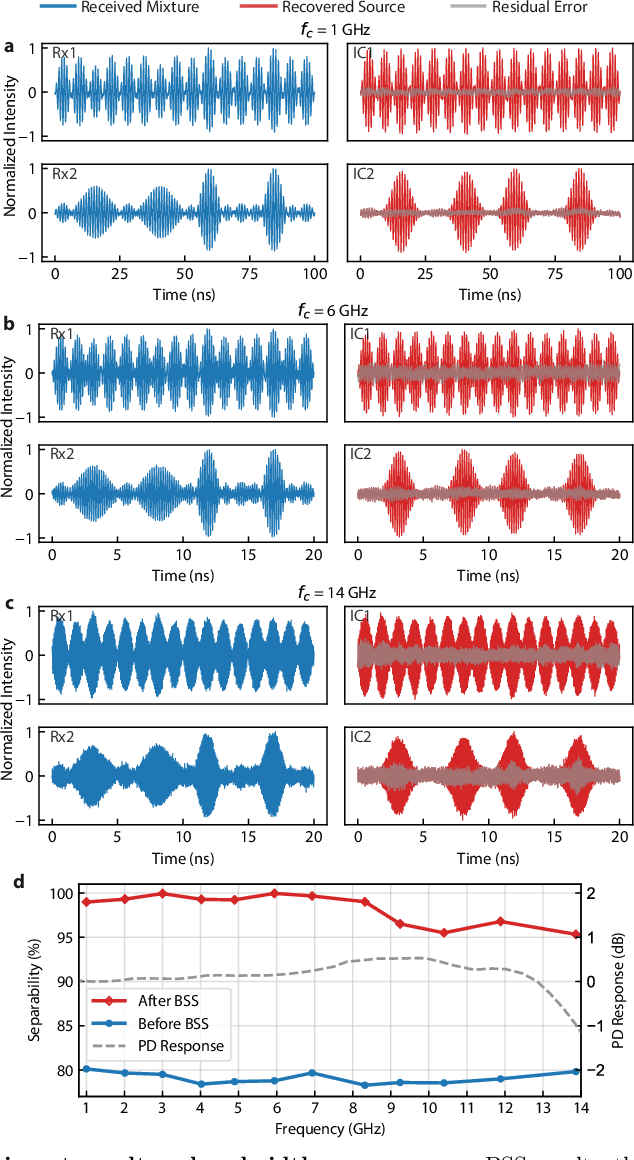
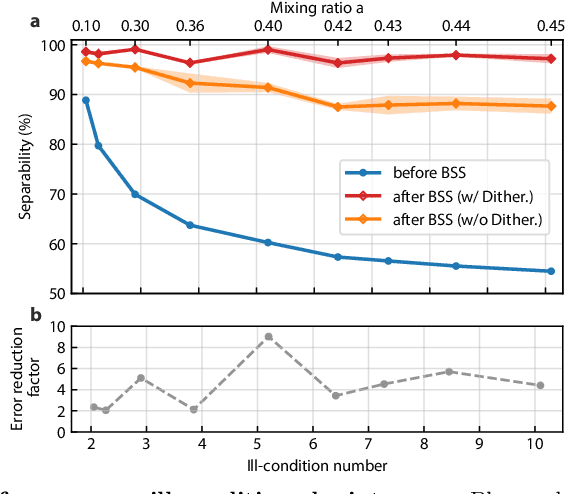
Abstract:The expansion of telecommunications incurs increasingly severe crosstalk and interference, and a physical layer cognitive method, called blind source separation (BSS), can effectively address these issues. BSS requires minimal prior knowledge to recover signals from their mixtures, agnostic to carrier frequency, signal format, and channel conditions. However, the previous BSS implemented in electronics did not fulfill this versatility due to the inherently narrow bandwidth of radio-frequency (RF) components, the high energy consumption of digital signal processors (DSP), and their shared weaknesses of low scalability. Here, we report a photonic BSS approach that inherits the advantages of optical devices and can fully fulfill its "blindness" aspect. Using a microring weight bank integrated on a photonic chip, we demonstrate energy-efficient, WDM-scalable BSS across 13.8 GHz of bandwidth, covering many standard frequency bands. Our system also has high (9-bit) accuracy for signal demixing thanks to a recently developed dithering control method, resulting in higher signal of interest ratios (SIR) even for ill-conditioned mixtures.
Silicon photonic-electronic neural network for fibre nonlinearity compensation
Oct 11, 2021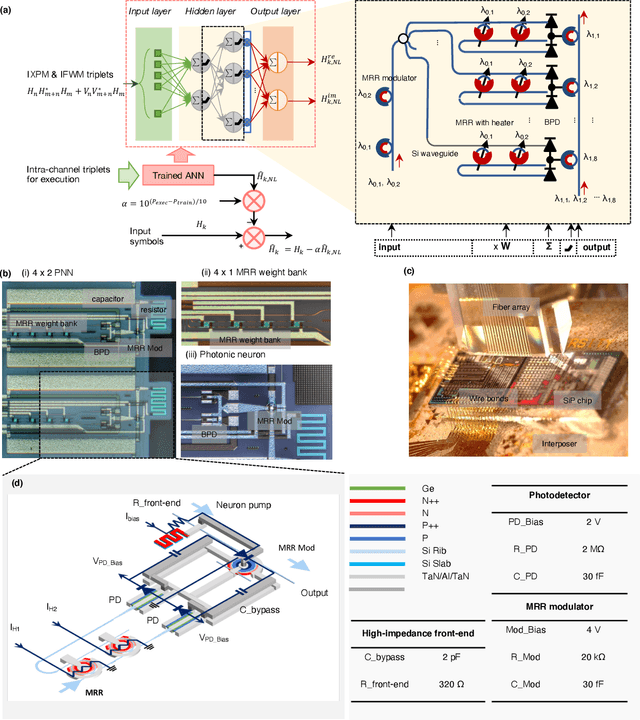
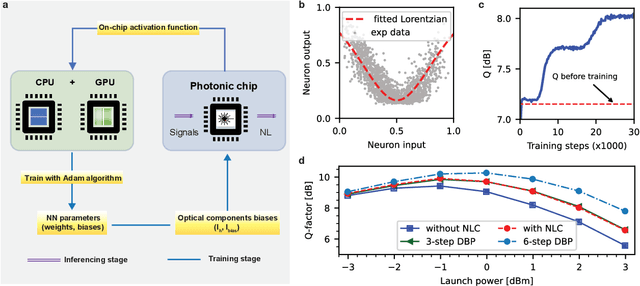
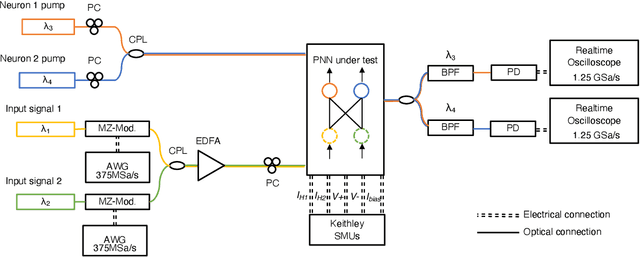
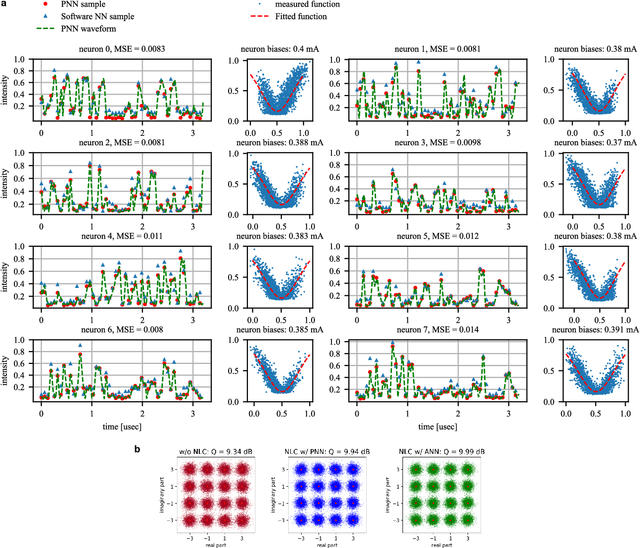
Abstract:In optical communication systems, fibre nonlinearity is the major obstacle in increasing the transmission capacity. Typically, digital signal processing techniques and hardware are used to deal with optical communication signals, but increasing speed and computational complexity create challenges for such approaches. Highly parallel, ultrafast neural networks using photonic devices have the potential to ease the requirements placed on the digital signal processing circuits by processing the optical signals in the analogue domain. Here we report a silicon photonice-lectronic neural network for solving fibre nonlinearity compensation of submarine optical fibre transmission systems. Our approach uses a photonic neural network based on wavelength-division multiplexing built on a CMOS-compatible silicon photonic platform. We show that the platform can be used to compensate optical fibre nonlinearities and improve the signal quality (Q)-factor in a 10,080 km submarine fibre communication system. The Q-factor improvement is comparable to that of a software-based neural network implemented on a 32-bit graphic processing unit-assisted workstation. Our reconfigurable photonic-electronic integrated neural network promises to address pressing challenges in high-speed intelligent signal processing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge