Aaditya Prakash Kattekola
mmSnap: Bayesian One-Shot Fusion in a Self-Calibrated mmWave Radar Network
May 01, 2025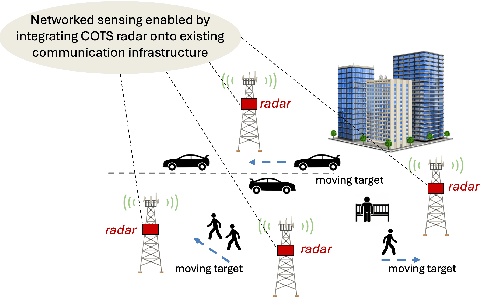
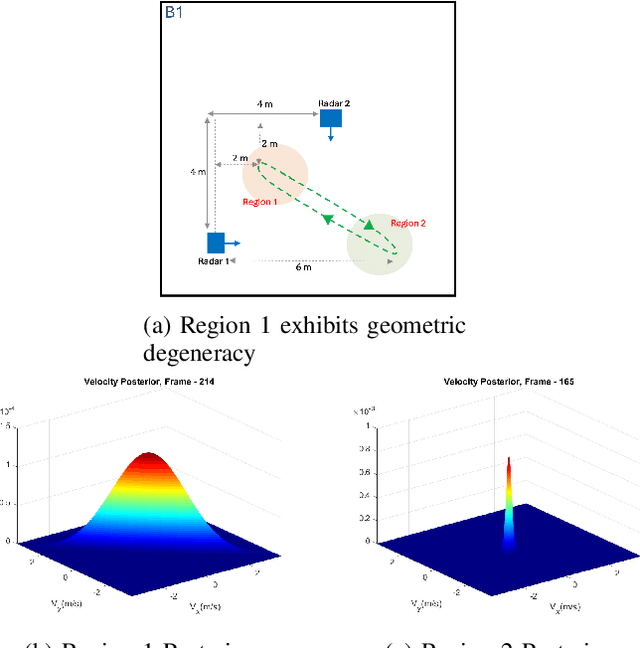
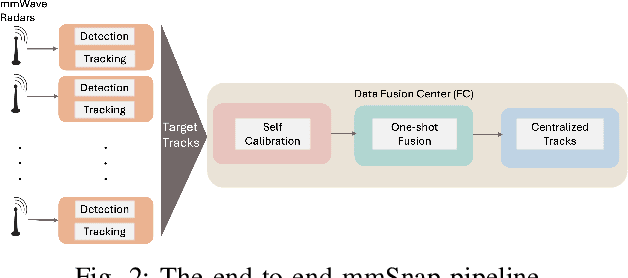
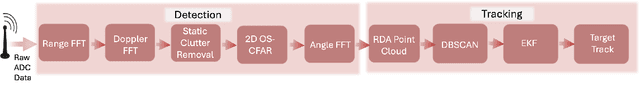
Abstract:We present mmSnap, a collaborative RF sensing framework using multiple radar nodes, and demonstrate its feasibility and efficacy using commercially available mmWave MIMO radars. Collaborative fusion requires network calibration, or estimates of the relative poses (positions and orientations) of the sensors. We experimentally validate a self-calibration algorithm developed in our prior work, which estimates relative poses in closed form by least squares matching of target tracks within the common field of view (FoV). We then develop and demonstrate a Bayesian framework for one-shot fusion of measurements from multiple calibrated nodes, which yields instantaneous estimates of position and velocity vectors that match smoothed estimates from multi-frame tracking. Our experiments, conducted outdoors with two radar nodes tracking a moving human target, validate the core assumptions required to develop a broader set of capabilities for networked sensing with opportunistically deployed nodes.
Crowd Size Estimation for Non-Uniform Spatial Distributions with mmWave Radar
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:Sensing with RF signals such as mmWave radar has gained considerable interest in recent years. This is particularly relevant to 6G networks, which aim to integrate sensing and communication (ISAC) capabilities for enhanced functionality. The contextual information provided by such sensing, whether collected by standalone non-ISAC units or integrated within ISAC, can not only optimize cellular network assets but can also serve as a valuable tool for a wide range of applications beyond network optimization. In this context, we present a novel methodology for crowd size estimation using monostatic mmWave radar, which is capable of accurately counting large crowds that are unevenly distributed across space. Our estimation approach relies on the rigorous derivation of occlusion probabilities, which are then used to mathematically characterize the probability distributions that describe the number of agents visible to the radar as a function of the crowd size. We then estimate the true crowd size by comparing these derived mathematical models to the empirical distribution of the number of visible agents detected by the radar. This method requires minimal sensing capabilities (e.g., angle-of-arrival information is not needed), thus being well suited for either a dedicated mmWave radar or an ISAC system. Extensive numerical simulations validate our methodology, demonstrating strong performance across diverse spatial distributions and for crowd sizes of up to (and including) 30 agents. We achieve a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.48 agents, significantly outperforming a baseline which assumes that the agents are uniformly distributed in the area. Overall, our approach holds significant promise for a variety of applications including network resource allocation, crowd management, and urban planning.
Performance Analysis of RIS-Aided NOMA Networks in $α-μ$ & $κ-μ$ Generalized Fading Channel
May 12, 2023Abstract:For forthcoming 5G networks, Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) is a very promising techniques. and in today's world, Line of Sight communication is becoming increasingly harder to achieve. Hence, technologies like Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) emerge. RIS-aided NOMA networks is a widely researched implementation of RIS. The environment where these networks are employed are non-homogeneous & non-linear in nature. The effectiveness of these systems must thus be evaluated using generalized fading channels. In this paper, the performance of a RIS-aided NOMA is compared with conventional NOMA in alpha-mu and kappa-mu channels. This paper also shows that the well-known fading distribution are special cases of these generalized fading channels, both analytically and through simulation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge