A. H. Beg
Tree Index: A New Cluster Evaluation Technique
Mar 24, 2020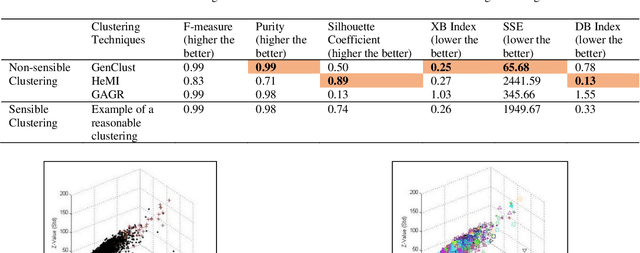
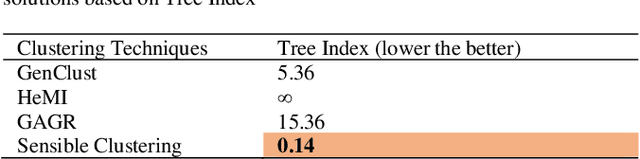
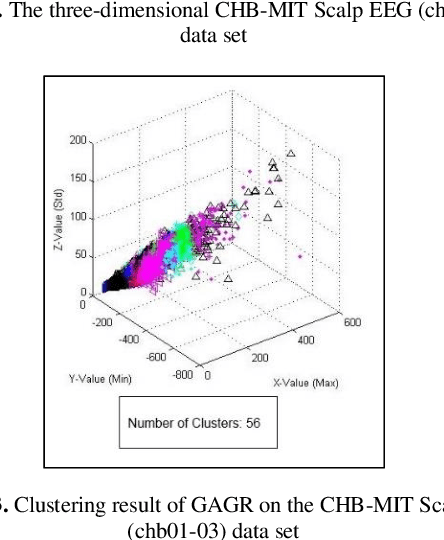

Abstract:We introduce a cluster evaluation technique called Tree Index. Our Tree Index algorithm aims at describing the structural information of the clustering rather than the quantitative format of cluster-quality indexes (where the representation power of clustering is some cumulative error similar to vector quantization). Our Tree Index is finding margins amongst clusters for easy learning without the complications of Minimum Description Length. Our Tree Index produces a decision tree from the clustered data set, using the cluster identifiers as labels. It combines the entropy of each leaf with their depth. Intuitively, a shorter tree with pure leaves generalizes the data well (the clusters are easy to learn because they are well separated). So, the labels are meaningful clusters. If the clustering algorithm does not separate well, trees learned from their results will be large and too detailed. We show that, on the clustering results (obtained by various techniques) on a brain dataset, Tree Index discriminates between reasonable and non-sensible clusters. We confirm the effectiveness of Tree Index through graphical visualizations. Tree Index evaluates the sensible solutions higher than the non-sensible solutions while existing cluster-quality indexes fail to do so.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge