İbrahim Hökelek
Design and Evaluation of Neural Network-Based Receiver Architectures for Reliable Communication
Mar 26, 2025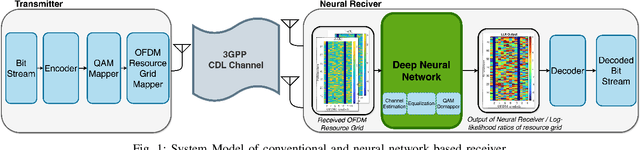
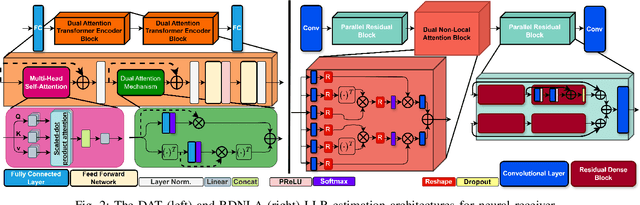
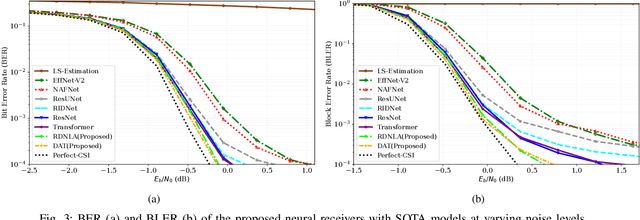
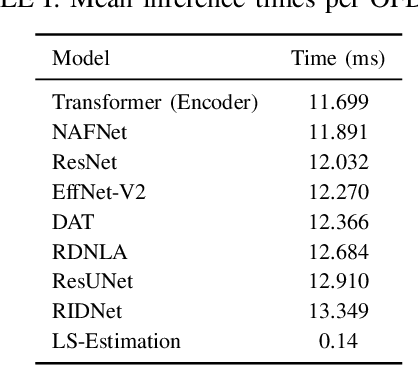
Abstract:Neural network-based receivers leverage deep learning to optimize signal detection and decoding, significantly improving bit-error rate (BER) and block-error rate (BLER) in challenging environments. This study evaluates various architectures and compares their BER and BLER performance across different noise levels. Two novel models, the Dual Attention Transformer (DAT) and the Residual Dual Non-Local Attention Network (RDNLA), integrate self-attention and residual learning to enhance signal reconstruction. These models bypass conventional channel estimation and equalization by directly predicting log-likelihood ratios (LLRs) from received signals, with noise variance as an additional input. Simulations show that DAT and RDNLA outperform traditional and other neural receiver models under varying signal-to-noise ratios (SNR), while their computational efficiency supports their feasibility for next-generation communication systems.
RIS Optimization Algorithms for Urban Wireless Scenarios in Sionna RT
Jan 10, 2025Abstract:This paper evaluates the performance of reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) optimization algorithms, which utilize channel estimation methods, in ray tracing (RT) simulations within urban digital twin environments. Beyond Sionna's native capabilities, we implement and benchmark additional RIS optimization algorithms based on channel estimation, enabling an evaluation of RIS strategies under various deployment conditions. Coverage maps for RIS-assisted communication systems are generated through the integration of Sionna's RT simulations. Moreover, real-world experimentation underscores the necessity of validating algorithms in near-realistic simulation environments, as minor variations in measurement setups can significantly affect performance.
Rapid CNN-Assisted Iterative RIS Element Configuration
Jul 21, 2023Abstract:Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs) are becoming one of the fundamental building blocks of next-generation wireless communication systems. To that end, RIS phase configuration optimization is an important issue, where finding the most suitable configuration becomes a challenging and resource-consuming task, especially as the number of RIS elements increases. Since exhaustive search is not practical, iterative algorithms are utilized to determine the RIS configuration by sequentially considering all RIS elements, where the best-performing phase shift configuration is obtained for each element. However, each configuration attempt requires receiver performance feedback, leading to higher delay and signaling overhead. Thus, in this paper, a convolutional neural network (CNN) based solution is formulated to rapidly find the phase configurations of the RIS elements. The simulation results for a RIS with $40\times40$ elements imply that the proposed algorithm reduces the number of steps dramatically e.g., from 3200 to 160 for the particular setup. Furthermore, such improvement in complexity is achieved with a slight degradation in performance.
Measurement-based Channel Characterization for A2A and A2G Wireless Drone Communication Systems
Jun 14, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents field measurement-based channel characterization for air--to--ground (A2G) and air--to--air (A2A) wireless communication systems using two drones equipped with lightweight software-defined radios. A correlation-based channel sounder is employed such that the transmitting drone broadcasts the sounding waveform with a pseudo-noise sequence and the receiving drone captures the sounding waveform together with the location information for the post-processing analysis. The path loss results demonstrate that the measurement and flat-earth two-ray results have similar trends for A2G while the measurement and free space path loss are similar to each other for A2A. The time delays between the direct path and multipath components are widely spread for A2A while the multipath components are mostly concentrated around the direct path for A2G generating a more challenging communication environment. We observe that the reflections from several buildings having metal roofs and claddings on the measurement site cause sudden peaks in the root-mean-square delay spread. The results indicate that the A2A channel has better characteristics than the A2G under similar mobility conditions.
Measurement-based Characterization of Physical Layer Security for RIS-assisted Wireless Systems
Dec 14, 2022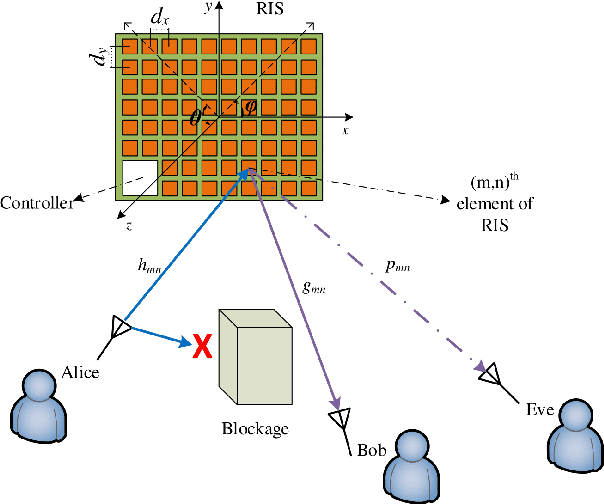
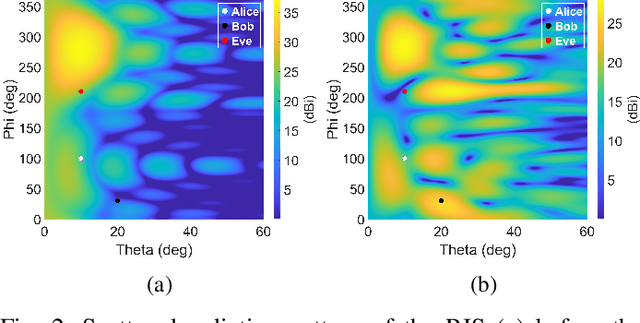
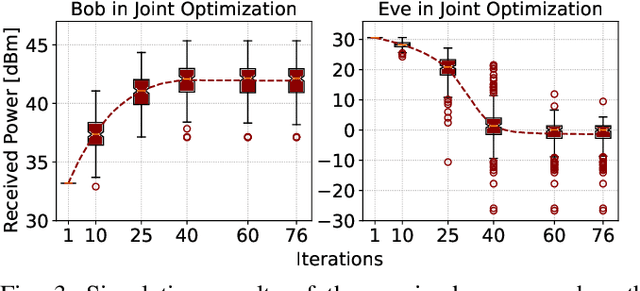
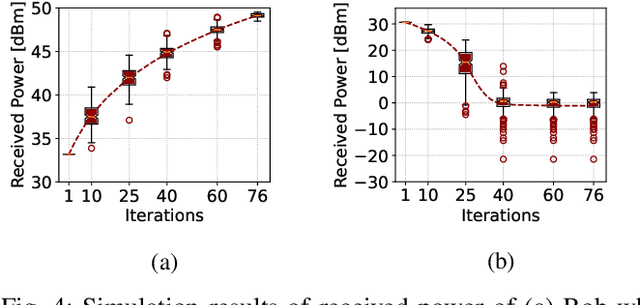
Abstract:There have been recently many studies demonstrating that the performance of wireless communication systems can be significantly improved by a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS), which is an attractive technology due to its low power requirement and low complexity. This paper presents a measurement-based characterization of RISs for providing physical layer security, where the transmitter (Alice), the intended user (Bob), and the eavesdropper (Eve) are deployed in an indoor environment. Each user is equipped with a software-defined radio connected to a horn antenna. The phase shifts of reflecting elements are software controlled to collaboratively determine the amount of received signal power at the locations of Bob and Eve in such a way that the secrecy capacity is aimed to be maximized. An iterative method is utilized to configure a Greenerwave RIS prototype consisting of 76 passive reflecting elements. Computer simulation and measurement results demonstrate that an RIS can be an effective tool to significantly increase the secrecy capacity between Bob and Eve.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge