Hüseyin Çevik
Design and Evaluation of Neural Network-Based Receiver Architectures for Reliable Communication
Mar 26, 2025
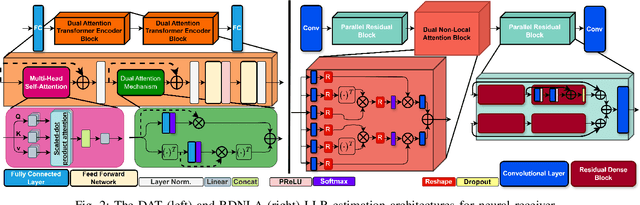
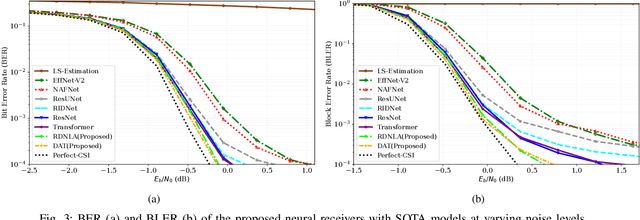
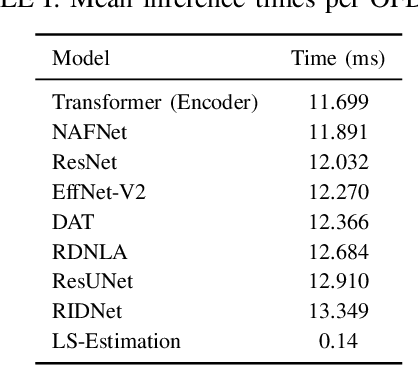
Abstract:Neural network-based receivers leverage deep learning to optimize signal detection and decoding, significantly improving bit-error rate (BER) and block-error rate (BLER) in challenging environments. This study evaluates various architectures and compares their BER and BLER performance across different noise levels. Two novel models, the Dual Attention Transformer (DAT) and the Residual Dual Non-Local Attention Network (RDNLA), integrate self-attention and residual learning to enhance signal reconstruction. These models bypass conventional channel estimation and equalization by directly predicting log-likelihood ratios (LLRs) from received signals, with noise variance as an additional input. Simulations show that DAT and RDNLA outperform traditional and other neural receiver models under varying signal-to-noise ratios (SNR), while their computational efficiency supports their feasibility for next-generation communication systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge