Zipf's law in 50 languages: its structural pattern, linguistic interpretation, and cognitive motivation
Paper and Code
Jul 05, 2018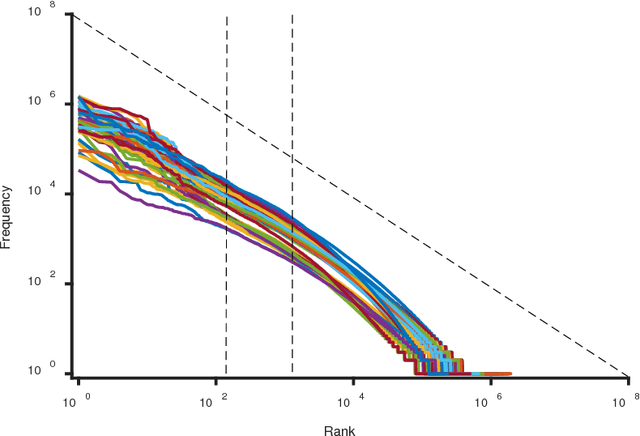
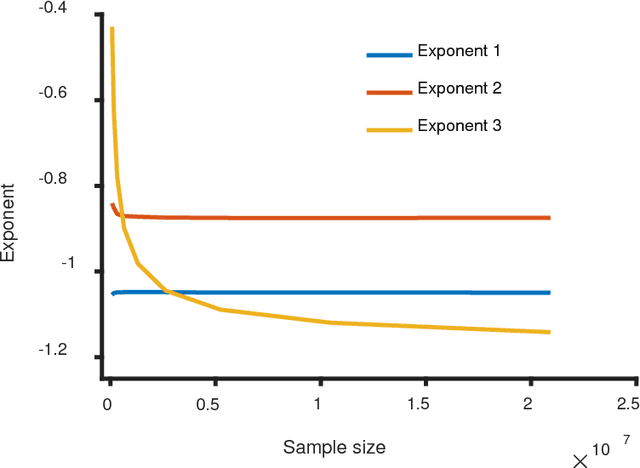
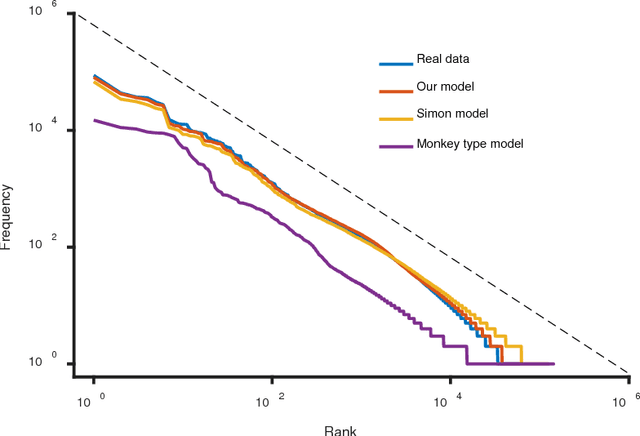
Zipf's law has been found in many human-related fields, including language, where the frequency of a word is persistently found as a power law function of its frequency rank, known as Zipf's law. However, there is much dispute whether it is a universal law or a statistical artifact, and little is known about what mechanisms may have shaped it. To answer these questions, this study conducted a large scale cross language investigation into Zipf's law. The statistical results show that Zipf's laws in 50 languages all share a 3-segment structural pattern, with each segment demonstrating distinctive linguistic properties and the lower segment invariably bending downwards to deviate from theoretical expectation. This finding indicates that this deviation is a fundamental and universal feature of word frequency distributions in natural languages, not the statistical error of low frequency words. A computer simulation based on the dual-process theory yields Zipf's law with the same structural pattern, suggesting that Zipf's law of natural languages are motivated by common cognitive mechanisms. These results show that Zipf's law in languages is motivated by cognitive mechanisms like dual-processing that govern human verbal behaviors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge