Zero-shot Entailment of Leaderboards for Empirical AI Research
Paper and Code
Mar 29, 2023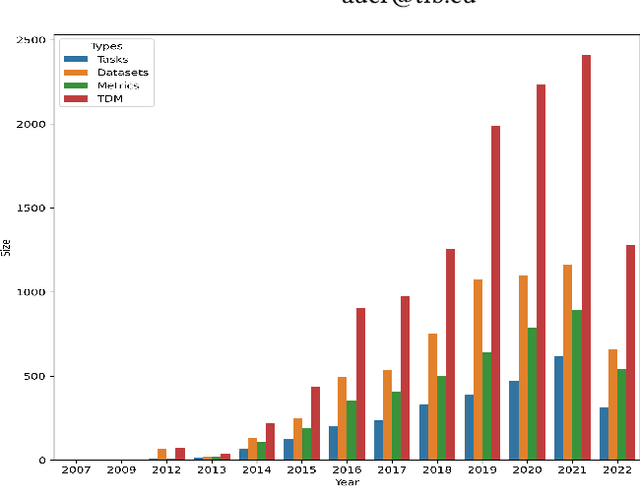
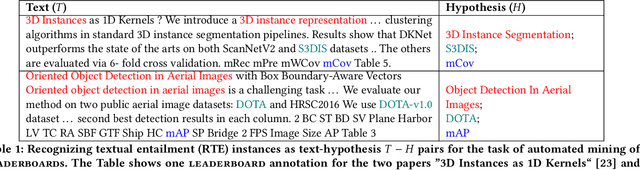
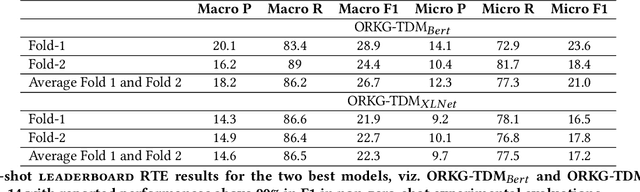
We present a large-scale empirical investigation of the zero-shot learning phenomena in a specific recognizing textual entailment (RTE) task category, i.e. the automated mining of leaderboards for Empirical AI Research. The prior reported state-of-the-art models for leaderboards extraction formulated as an RTE task, in a non-zero-shot setting, are promising with above 90% reported performances. However, a central research question remains unexamined: did the models actually learn entailment? Thus, for the experiments in this paper, two prior reported state-of-the-art models are tested out-of-the-box for their ability to generalize or their capacity for entailment, given leaderboard labels that were unseen during training. We hypothesize that if the models learned entailment, their zero-shot performances can be expected to be moderately high as well--perhaps, concretely, better than chance. As a result of this work, a zero-shot labeled dataset is created via distant labeling formulating the leaderboard extraction RTE task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge