XL-Editor: Post-editing Sentences with XLNet
Paper and Code
Oct 19, 2019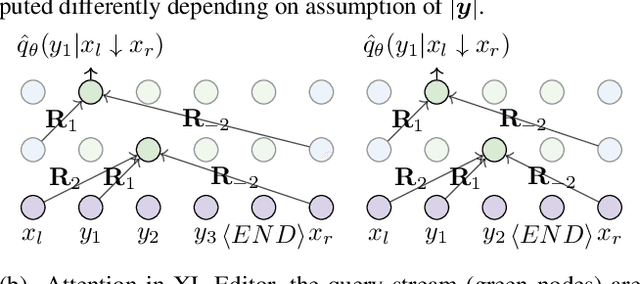
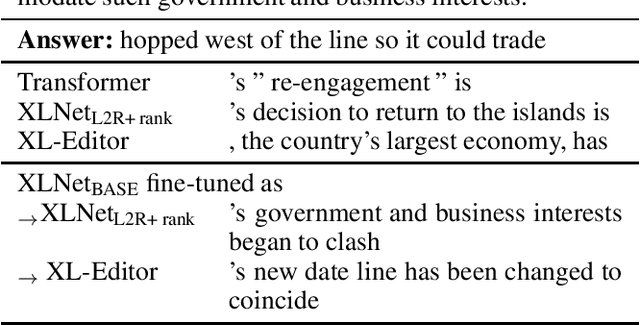
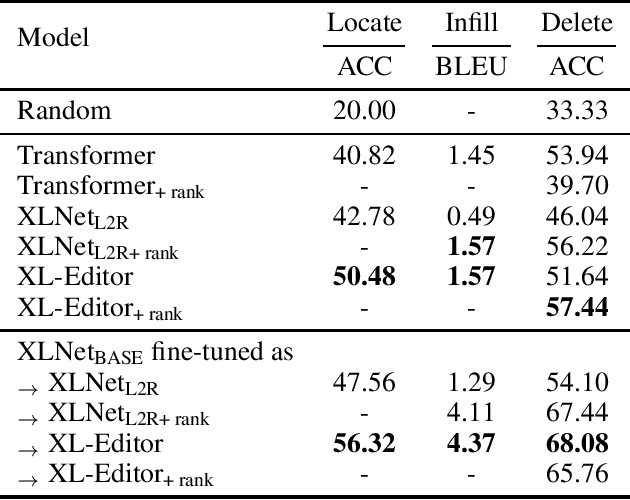

While neural sequence generation models achieve initial success for many NLP applications, the canonical decoding procedure with left-to-right generation order (i.e., autoregressive) in one-pass can not reflect the true nature of human revising a sentence to obtain a refined result. In this work, we propose XL-Editor, a novel training framework that enables state-of-the-art generalized autoregressive pretraining methods, XLNet specifically, to revise a given sentence by the variable-length insertion probability. Concretely, XL-Editor can (1) estimate the probability of inserting a variable-length sequence into a specific position of a given sentence; (2) execute post-editing operations such as insertion, deletion, and replacement based on the estimated variable-length insertion probability; (3) complement existing sequence-to-sequence models to refine the generated sequences. Empirically, we first demonstrate better post-editing capabilities of XL-Editor over XLNet on the text insertion and deletion tasks, which validates the effectiveness of our proposed framework. Furthermore, we extend XL-Editor to the unpaired text style transfer task, where transferring the target style onto a given sentence can be naturally viewed as post-editing the sentence into the target style. XL-Editor achieves significant improvement in style transfer accuracy and also maintains coherent semantic of the original sentence, showing the broad applicability of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge