Wormhole Loss for Partial Shape Matching
Paper and Code
Oct 30, 2024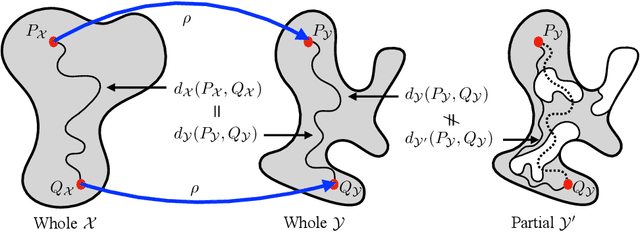

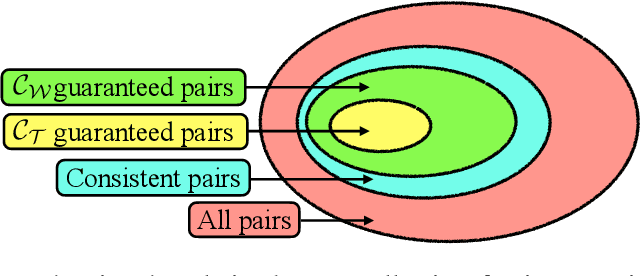
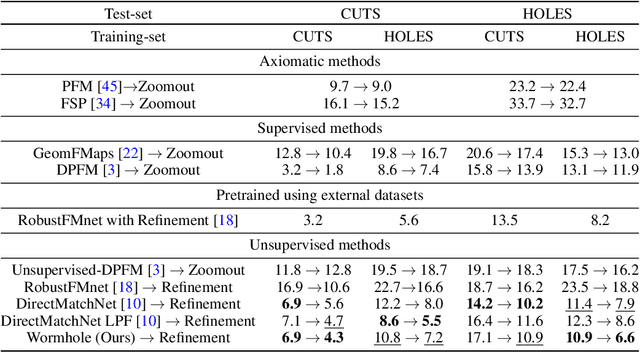
When matching parts of a surface to its whole, a fundamental question arises: Which points should be included in the matching process? The issue is intensified when using isometry to measure similarity, as it requires the validation of whether distances measured between pairs of surface points should influence the matching process. The approach we propose treats surfaces as manifolds equipped with geodesic distances, and addresses the partial shape matching challenge by introducing a novel criterion to meticulously search for consistent distances between pairs of points. The new criterion explores the relation between intrinsic geodesic distances between the points, geodesic distances between the points and surface boundaries, and extrinsic distances between boundary points measured in the embedding space. It is shown to be less restrictive compared to previous measures and achieves state-of-the-art results when used as a loss function in training networks for partial shape matching.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge