Word Recognition, Competition, and Activation in a Model of Visually Grounded Speech
Paper and Code
Sep 18, 2019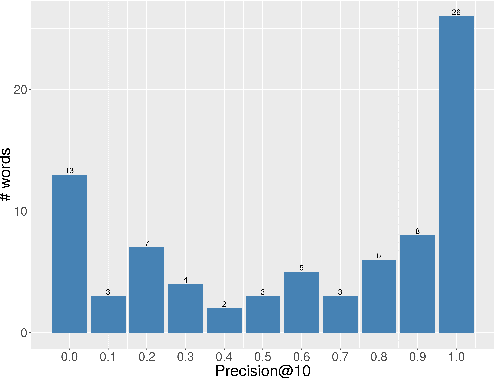
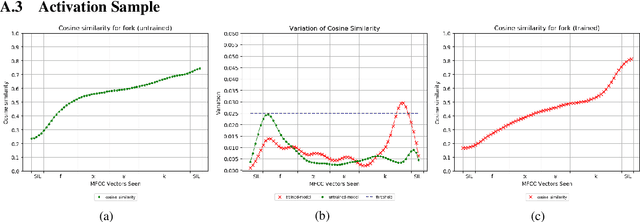
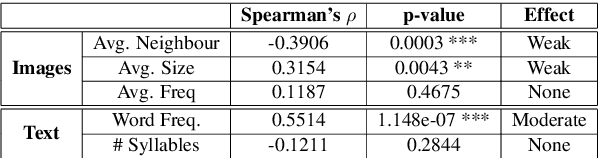
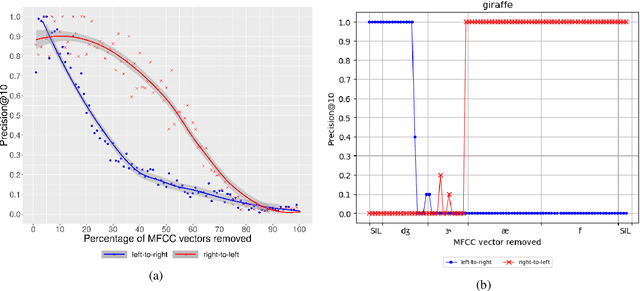
In this paper, we study how word-like units are represented and activated in a recurrent neural model of visually grounded speech. The model used in our experiments is trained to project an image and its spoken description in a common representation space. We show that a recurrent model trained on spoken sentences implicitly segments its input into word-like units and reliably maps them to their correct visual referents. We introduce a methodology originating from linguistics to analyse the representation learned by neural networks -- the gating paradigm -- and show that the correct representation of a word is only activated if the network has access to first phoneme of the target word, suggesting that the network does not rely on a global acoustic pattern. Furthermore, we find out that not all speech frames (MFCC vectors in our case) play an equal role in the final encoded representation of a given word, but that some frames have a crucial effect on it. Finally, we suggest that word representation could be activated through a process of lexical competition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge