Widening siamese architectures for stereo matching
Paper and Code
Nov 01, 2017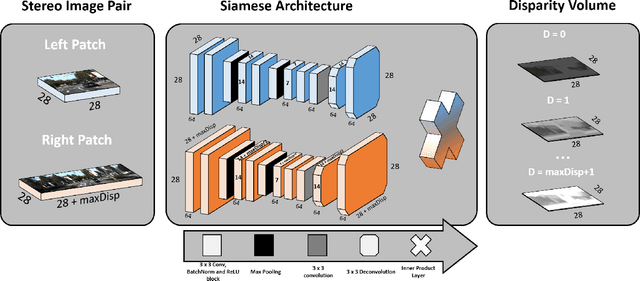

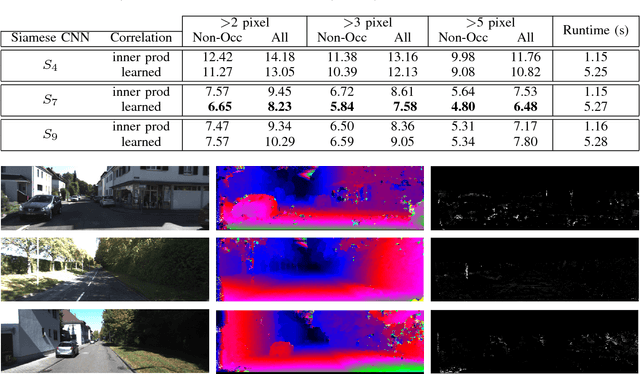
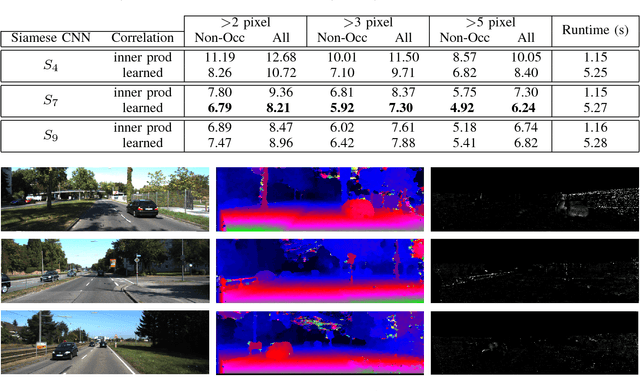
Computational stereo is one of the classical problems in computer vision. Numerous algorithms and solutions have been reported in recent years focusing on developing methods for computing similarity, aggregating it to obtain spatial support and finally optimizing an energy function to find the final disparity. In this paper, we focus on the feature extraction component of stereo matching architecture and we show standard CNNs operation can be used to improve the quality of the features used to find point correspondences. Furthermore, we propose a simple space aggregation that hugely simplifies the correlation learning problem. Our results on benchmark data are compelling and show promising potential even without refining the solution.
* 7 pages, 4 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge