Why Normalizing Flows Fail to Detect Out-of-Distribution Data
Paper and Code
Jun 15, 2020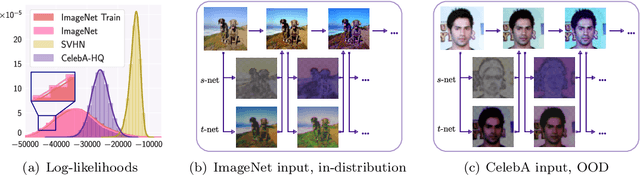
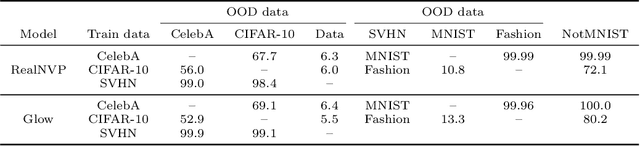


Detecting out-of-distribution (OOD) data is crucial for robust machine learning systems. Normalizing flows are flexible deep generative models that often surprisingly fail to distinguish between in- and out-of-distribution data: a flow trained on pictures of clothing assigns higher likelihood to handwritten digits. We investigate why normalizing flows perform poorly for OOD detection. We demonstrate that flows learn local pixel correlations and generic image-to-latent-space transformations which are not specific to the target image dataset. We show that by modifying the architecture of flow coupling layers we can bias the flow towards learning the semantic structure of the target data, improving OOD detection. Our investigation reveals that properties that enable flows to generate high-fidelity images can have a detrimental effect on OOD detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge