Why Linguistics Will Thrive in the 21st Century: A Reply to Piantadosi
Paper and Code
Aug 06, 2023
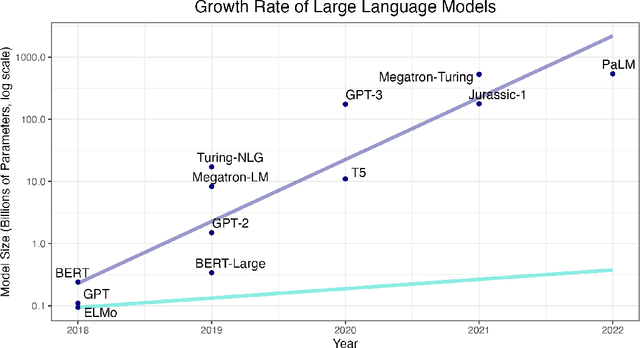
We present a critical assessment of Piantadosi's (2023) claim that "Modern language models refute Chomsky's approach to language," focusing on four main points. First, despite the impressive performance and utility of large language models (LLMs), humans achieve their capacity for language after exposure to several orders of magnitude less data. The fact that young children become competent, fluent speakers of their native languages with relatively little exposure to them is the central mystery of language learning to which Chomsky initially drew attention, and LLMs currently show little promise of solving this mystery. Second, what can the artificial reveal about the natural? Put simply, the implications of LLMs for our understanding of the cognitive structures and mechanisms underlying language and its acquisition are like the implications of airplanes for understanding how birds fly. Third, LLMs cannot constitute scientific theories of language for several reasons, not least of which is that scientific theories must provide interpretable explanations, not just predictions. This leads to our final point: to even determine whether the linguistic and cognitive capabilities of LLMs rival those of humans requires explicating what humans' capacities actually are. In other words, it requires a separate theory of language and cognition; generative linguistics provides precisely such a theory. As such, we conclude that generative linguistics as a scientific discipline will remain indispensable throughout the 21st century and beyond.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge