When are Deep Networks really better than Random Forests at small sample sizes?
Paper and Code
Aug 31, 2021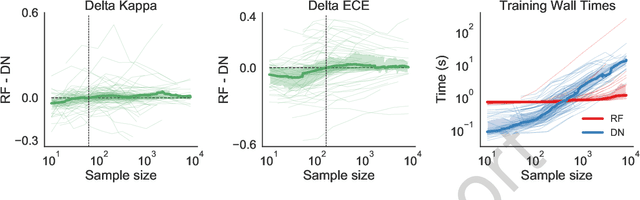
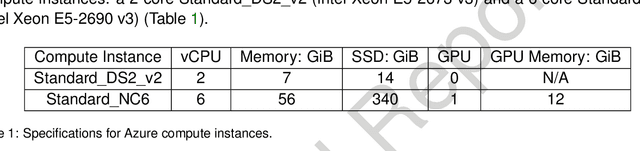

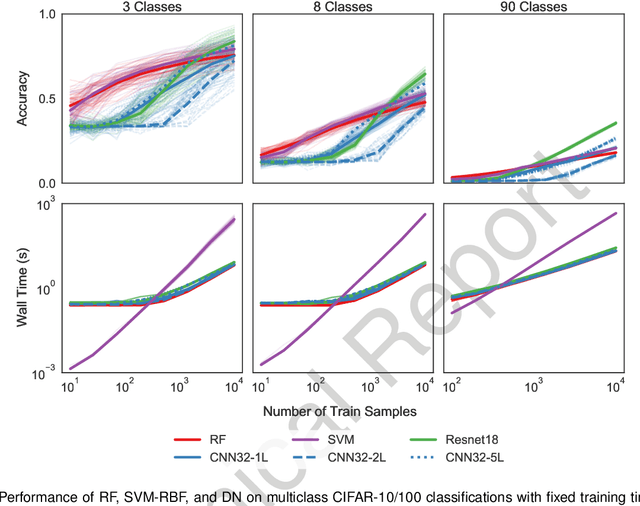
Random forests (RF) and deep networks (DN) are two of the most popular machine learning methods in the current scientific literature and yield differing levels of performance on different data modalities. We wish to further explore and establish the conditions and domains in which each approach excels, particularly in the context of sample size and feature dimension. To address these issues, we tested the performance of these approaches across tabular, image, and audio settings using varying model parameters and architectures. Our focus is on datasets with at most 10,000 samples, which represent a large fraction of scientific and biomedical datasets. In general, we found RF to excel at tabular and structured data (image and audio) with small sample sizes, whereas DN performed better on structured data with larger sample sizes. Although we plan to continue updating this technical report in the coming months, we believe the current preliminary results may be of interest to others.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge