What's the Opposite of a Face? Finding Shared Decodable Concepts and their Negations in the Brain
Paper and Code
May 27, 2024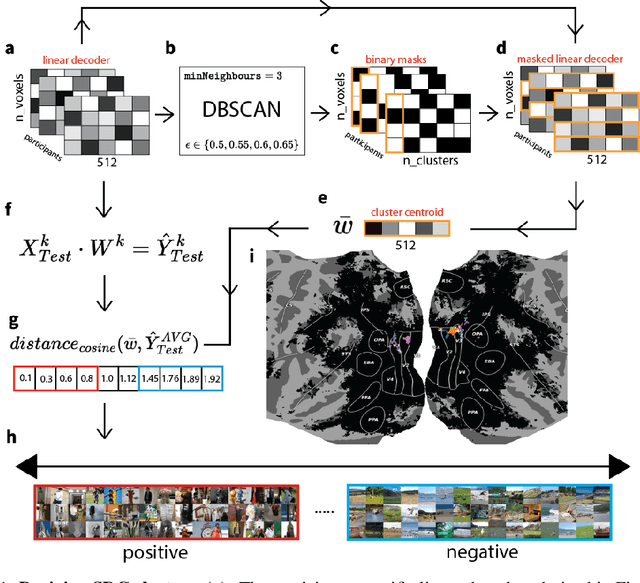
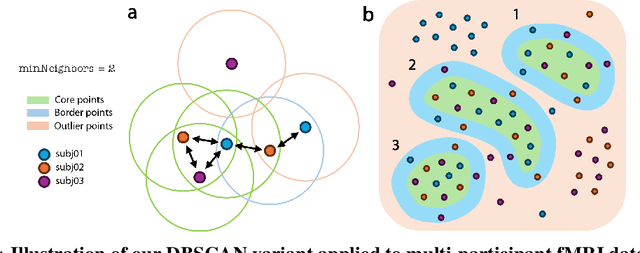
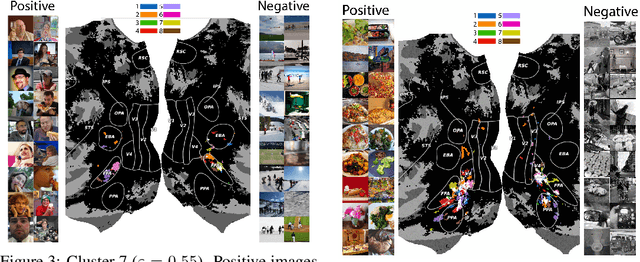
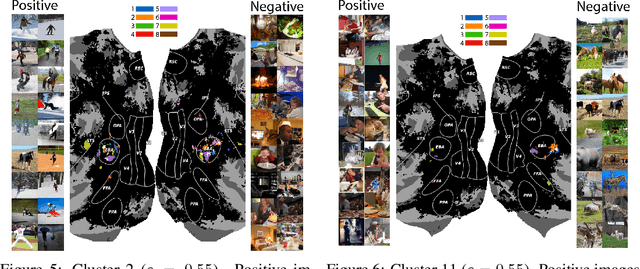
Prior work has offered evidence for functional localization in the brain; different anatomical regions preferentially activate for certain types of visual input. For example, the fusiform face area preferentially activates for visual stimuli that include a face. However, the spectrum of visual semantics is extensive, and only a few semantically-tuned patches of cortex have so far been identified in the human brain. Using a multimodal (natural language and image) neural network architecture (CLIP) we train a highly accurate contrastive model that maps brain responses during naturalistic image viewing to CLIP embeddings. We then use a novel adaptation of the DBSCAN clustering algorithm to cluster the parameters of these participant-specific contrastive models. This reveals what we call Shared Decodable Concepts (SDCs): clusters in CLIP space that are decodable from common sets of voxels across multiple participants. Examining the images most and least associated with each SDC cluster gives us additional insight into the semantic properties of each SDC. We note SDCs for previously reported visual features (e.g. orientation tuning in early visual cortex) as well as visual semantic concepts such as faces, places and bodies. In cases where our method finds multiple clusters for a visuo-semantic concept, the least associated images allow us to dissociate between confounding factors. For example, we discovered two clusters of food images, one driven by color, the other by shape. We also uncover previously unreported areas such as regions of extrastriate body area (EBA) tuned for legs/hands and sensitivity to numerosity in right intraparietal sulcus, and more. Thus, our contrastive-learning methodology better characterizes new and existing visuo-semantic representations in the brain by leveraging multimodal neural network representations and a novel adaptation of clustering algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge