What Can Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Movements in RAMIS Tell Us?
Paper and Code
Oct 16, 2017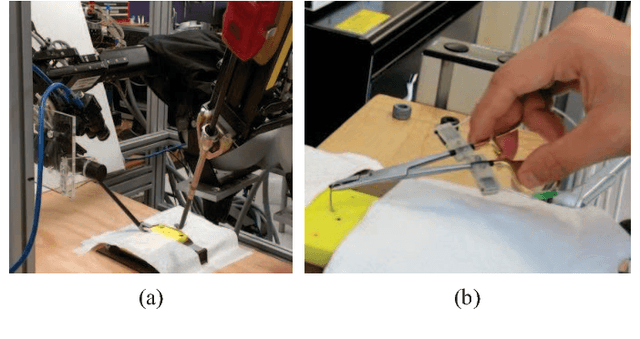



Quantitative characterization of surgical movements can improve the quality of patient care by informing the development of new training protocols for surgeons, and the design and control of surgical robots. Here, we present a novel characterization of open and teleoperated suturing movements that is based on principles from computational motor control. We focus on the extensively-studied relationship between the speed of movement and its geometry. In three-dimensional movements, this relationship is defined by the one-sixth power law that relates between the speed, the curvature, and the torsion of movement trajectories. We fitted the parameters of the one-sixth power law to suturing movements of participants with different levels of surgical experience in open (using sensorized forceps) and teleoperated (using the da Vinci Research Kit / da Vinci Surgical System) conditions from two different datasets. We found that teleoperation significantly affected the parameters of the power law, and that there were large differences between different stages of movement. These results open a new avenue for studying the effect of teleoperation on the spatiotemporal characteristics of the movements of surgeons, and lay the foundation for the development of new algorithms for automatic segmentation of surgical tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge