What can phylogenetic metrics tell us about useful diversity in evolutionary algorithms?
Paper and Code
Aug 28, 2021
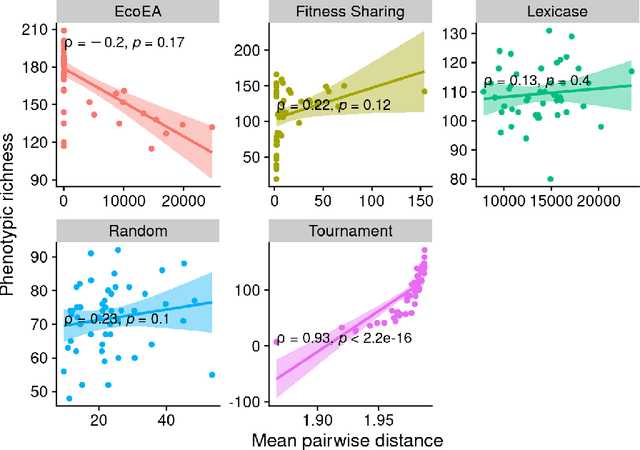
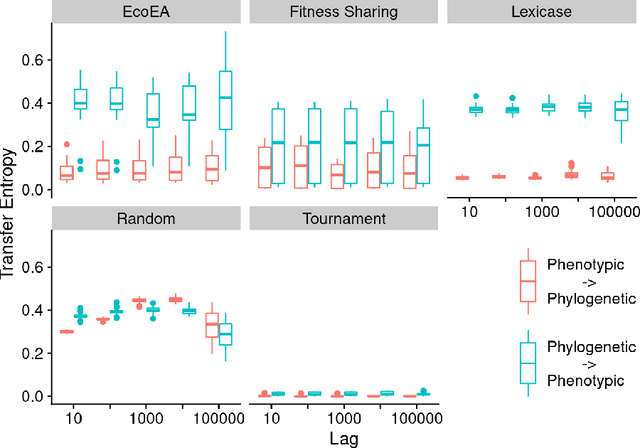
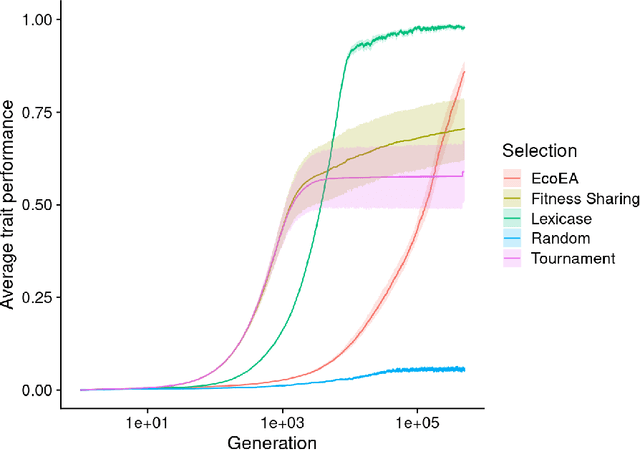
It is generally accepted that "diversity" is associated with success in evolutionary algorithms. However, diversity is a broad concept that can be measured and defined in a multitude of ways. To date, most evolutionary computation research has measured diversity using the richness and/or evenness of a particular genotypic or phenotypic property. While these metrics are informative, we hypothesize that other diversity metrics are more strongly predictive of success. Phylogenetic diversity metrics are a class of metrics popularly used in biology, which take into account the evolutionary history of a population. Here, we investigate the extent to which 1) these metrics provide different information than those traditionally used in evolutionary computation, and 2) these metrics better predict the long-term success of a run of evolutionary computation. We find that, in most cases, phylogenetic metrics behave meaningfully differently from other diversity metrics. Moreover, our results suggest that phylogenetic diversity is indeed a better predictor of success.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge