What Can Knowledge Bring to Machine Learning? -- A Survey of Low-shot Learning for Structured Data
Paper and Code
Jun 11, 2021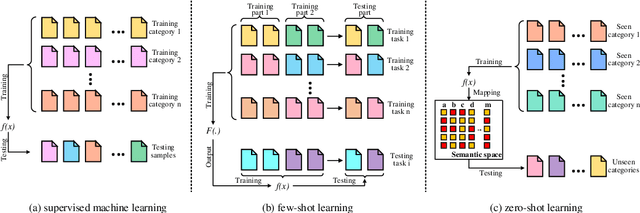


Supervised machine learning has several drawbacks that make it difficult to use in many situations. Drawbacks include: heavy reliance on massive training data, limited generalizability and poor expressiveness of high-level semantics. Low-shot Learning attempts to address these drawbacks. Low-shot learning allows the model to obtain good predictive power with very little or no training data, where structured knowledge plays a key role as a high-level semantic representation of human. This article will review the fundamental factors of low-shot learning technologies, with a focus on the operation of structured knowledge under different low-shot conditions. We also introduce other techniques relevant to low-shot learning. Finally, we point out the limitations of low-shot learning, the prospects and gaps of industrial applications, and future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge