Weisfeiler-Lehman meets Gromov-Wasserstein
Paper and Code
Feb 05, 2022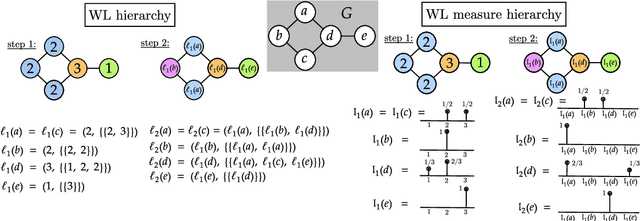
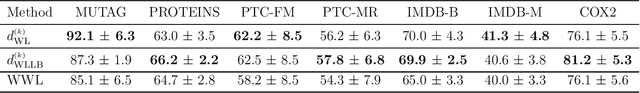

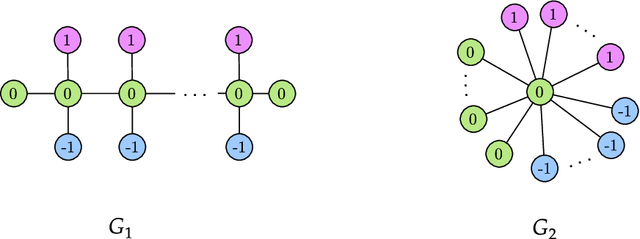
The Weisfeiler-Lehman (WL) test is a classical procedure for graph isomorphism testing. The WL test has also been widely used both for designing graph kernels and for analyzing graph neural networks. In this paper, we propose the Weisfeiler-Lehman (WL) distance, a notion of distance between labeled measure Markov chains (LMMCs), of which labeled graphs are special cases. The WL distance is polynomial time computable and is also compatible with the WL test in the sense that the former is positive if and only if the WL test can distinguish the two involved graphs. The WL distance captures and compares subtle structures of the underlying LMMCs and, as a consequence of this, it is more discriminating than the distance between graphs used for defining the state-of-the-art Wasserstein Weisfeiler-Lehman graph kernel. Inspired by the structure of the WL distance we identify a neural network architecture on LMMCs which turns out to be universal w.r.t. continuous functions defined on the space of all LMMCs (which includes all graphs) endowed with the WL distance. Finally, the WL distance turns out to be stable w.r.t. a natural variant of the Gromov-Wasserstein (GW) distance for comparing metric Markov chains that we identify. Hence, the WL distance can also be construed as a polynomial time lower bound for the GW distance which is in general NP-hard to compute.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge