Weakly Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Vestibular Schwannoma Segmentation
Paper and Code
Mar 13, 2023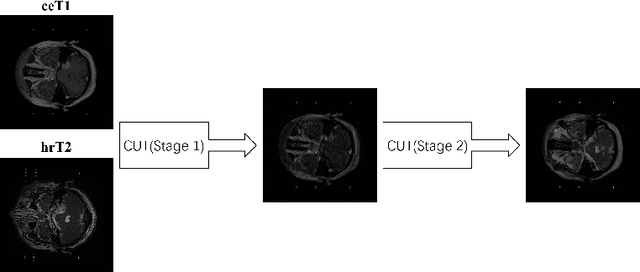



Vestibular schwannoma (VS) is a non-cancerous tumor located next to the ear that can cause hearing loss. Most brain MRI images acquired from patients are contrast-enhanced T1 (ceT1), with a growing interest in high-resolution T2 images (hrT2) to replace ceT1, which involves the use of a contrast agent. As hrT2 images are currently scarce, it is less likely to train robust machine learning models to segment VS or other brain structures. In this work, we propose a weakly supervised machine learning approach that learns from only ceT1 scans and adapts to segment two structures from hrT2 scans: the VS and the cochlea from the crossMoDA dataset. Our model 1) generates fake hrT2 scans from ceT1 images and segmentation masks, 2) is trained using the fake hrT2 scans, 3) predicts the augmented real hrT2 scans, and 4) is retrained again using both the fake and real hrT2. The final result of this model has been computed on an unseen testing dataset provided by the 2022 crossMoDA challenge organizers. The mean dice score and average symmetric surface distance (ASSD) are 0.78 and 0.46, respectively. The predicted segmentation masks achieved a dice score of 0.83 and an ASSD of 0.56 on the VS, and a dice score of 0.74 and an ASSD of 0.35 on the cochleas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge