Wavelet Scattering Transform for Improving Generalization in Low-Resourced Spoken Language Identification
Paper and Code
Oct 03, 2023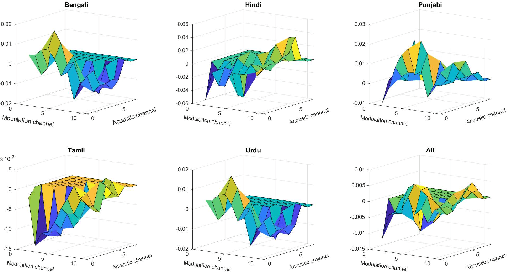

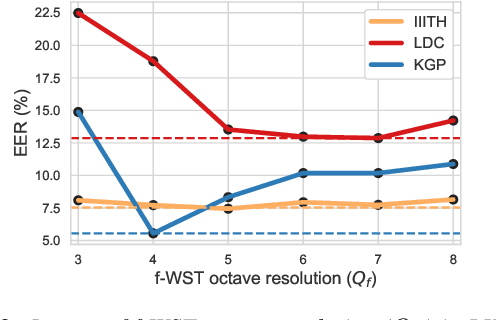

Commonly used features in spoken language identification (LID), such as mel-spectrogram or MFCC, lose high-frequency information due to windowing. The loss further increases for longer temporal contexts. To improve generalization of the low-resourced LID systems, we investigate an alternate feature representation, wavelet scattering transform (WST), that compensates for the shortcomings. To our knowledge, WST is not explored earlier in LID tasks. We first optimize WST features for multiple South Asian LID corpora. We show that LID requires low octave resolution and frequency-scattering is not useful. Further, cross-corpora evaluations show that the optimal WST hyper-parameters depend on both train and test corpora. Hence, we develop fused ECAPA-TDNN based LID systems with different sets of WST hyper-parameters to improve generalization for unknown data. Compared to MFCC, EER is reduced upto 14.05% and 6.40% for same-corpora and blind VoxLingua107 evaluations, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge