VQ-ACE: Efficient Policy Search for Dexterous Robotic Manipulation via Action Chunking Embedding
Paper and Code
Nov 05, 2024

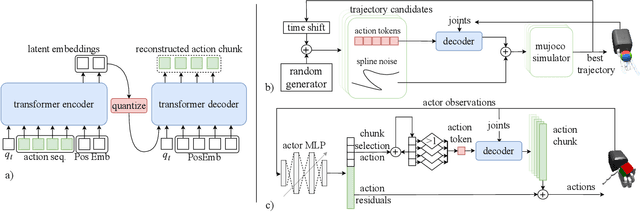

Dexterous robotic manipulation remains a significant challenge due to the high dimensionality and complexity of hand movements required for tasks like in-hand manipulation and object grasping. This paper addresses this issue by introducing Vector Quantized Action Chunking Embedding (VQ-ACE), a novel framework that compresses human hand motion into a quantized latent space, significantly reducing the action space's dimensionality while preserving key motion characteristics. By integrating VQ-ACE with both Model Predictive Control (MPC) and Reinforcement Learning (RL), we enable more efficient exploration and policy learning in dexterous manipulation tasks using a biomimetic robotic hand. Our results show that latent space sampling with MPC produces more human-like behavior in tasks such as Ball Rolling and Object Picking, leading to higher task success rates and reduced control costs. For RL, action chunking accelerates learning and improves exploration, demonstrated through faster convergence in tasks like cube stacking and in-hand cube reorientation. These findings suggest that VQ-ACE offers a scalable and effective solution for robotic manipulation tasks involving complex, high-dimensional state spaces, contributing to more natural and adaptable robotic systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge