Visually Supervised Speaker Detection and Localization via Microphone Array
Paper and Code
Mar 07, 2022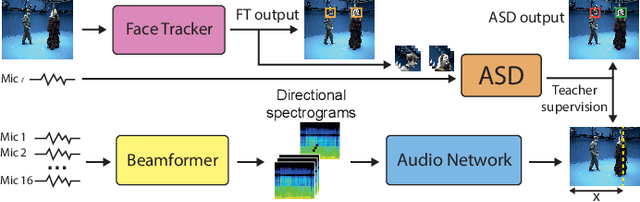
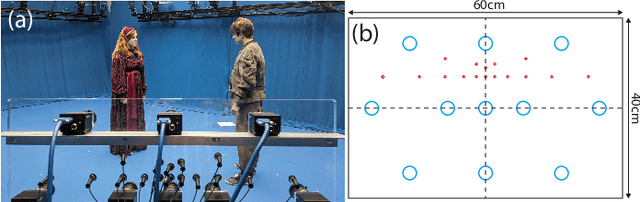
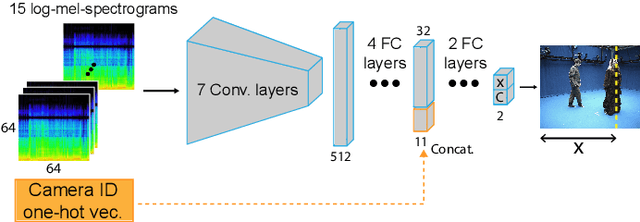
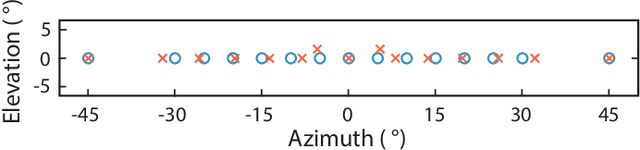
Active speaker detection (ASD) is a multi-modal task that aims to identify who, if anyone, is speaking from a set of candidates. Current audio-visual approaches for ASD typically rely on visually pre-extracted face tracks (sequences of consecutive face crops) and the respective monaural audio. However, their recall rate is often low as only the visible faces are included in the set of candidates. Monaural audio may successfully detect the presence of speech activity but fails in localizing the speaker due to the lack of spatial cues. Our solution extends the audio front-end using a microphone array. We train an audio convolutional neural network (CNN) in combination with beamforming techniques to regress the speaker's horizontal position directly in the video frames. We propose to generate weak labels using a pre-trained active speaker detector on pre-extracted face tracks. Our pipeline embraces the "student-teacher" paradigm, where a trained "teacher" network is used to produce pseudo-labels visually. The "student" network is an audio network trained to generate the same results. At inference, the student network can independently localize the speaker in the visual frames directly from the audio input. Experimental results on newly collected data prove that our approach significantly outperforms a variety of other baselines as well as the teacher network itself. It results in an excellent speech activity detector too.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge