Video Restoration with a Deep Plug-and-Play Prior
Paper and Code
Sep 15, 2022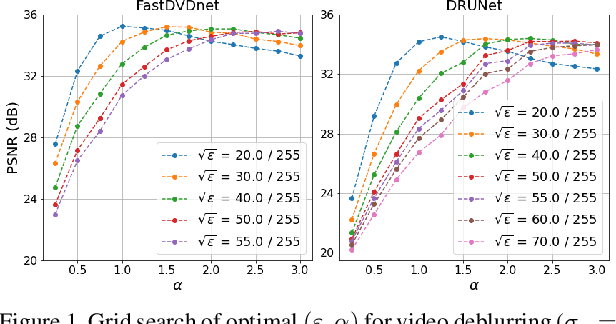
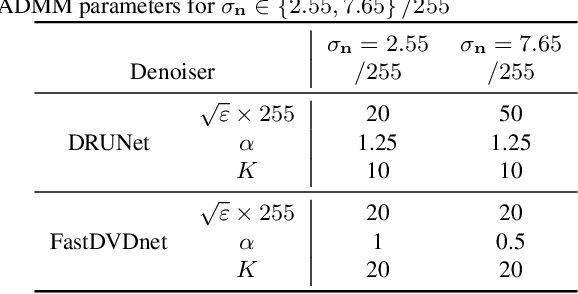
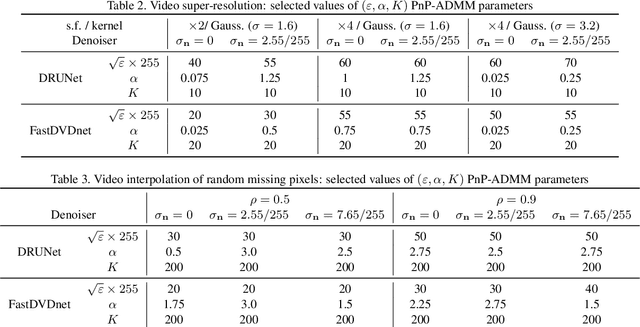
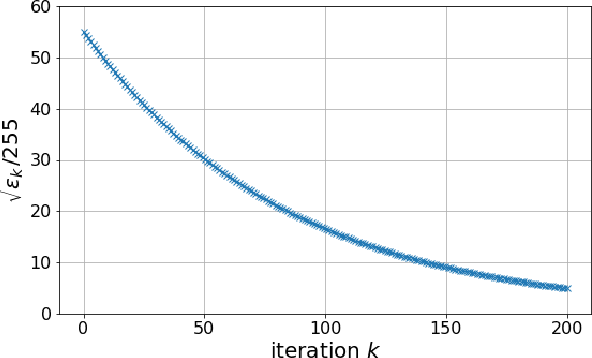
This paper presents a novel method for restoring digital videos via a Deep Plug-and-Play (PnP) approach. Under a Bayesian formalism, the method consists in using a deep convolutional denoising network in place of the proximal operator of the prior in an alternating optimization scheme. We distinguish ourselves from prior PnP work by directly applying that method to restore a digital video from a degraded video observation. This way, a network trained once for denoising can be repurposed for other video restoration tasks. Our experiments in video deblurring, super-resolution, and interpolation of random missing pixels all show a clear benefit to using a network specifically designed for video denoising, as it yields better restoration performance and better temporal stability than a single image network with similar denoising performance using the same PnP formulation. Moreover, our method compares favorably to applying a different state-of-the-art PnP scheme separately on each frame of the sequence. This opens new perspectives in the field of video restoration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge