Verifying Inverse Model Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Feb 04, 2022

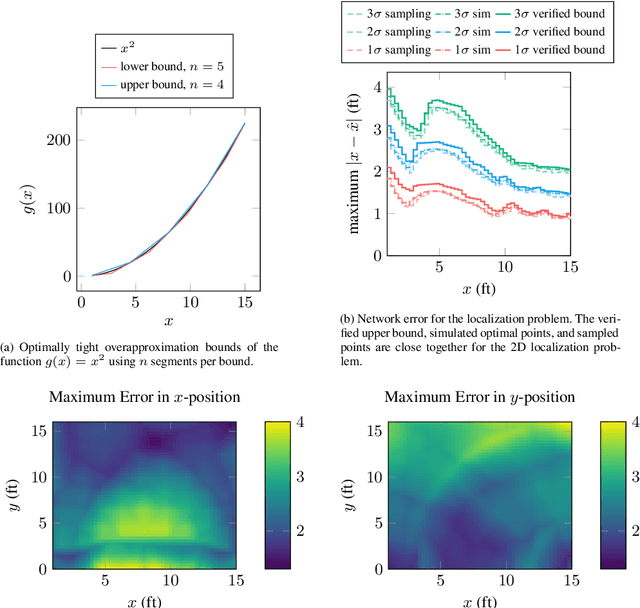
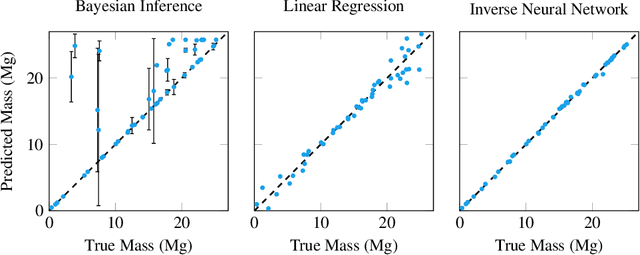
Inverse problems exist in a wide variety of physical domains from aerospace engineering to medical imaging. The goal is to infer the underlying state from a set of observations. When the forward model that produced the observations is nonlinear and stochastic, solving the inverse problem is very challenging. Neural networks are an appealing solution for solving inverse problems as they can be trained from noisy data and once trained are computationally efficient to run. However, inverse model neural networks do not have guarantees of correctness built-in, which makes them unreliable for use in safety and accuracy-critical contexts. In this work we introduce a method for verifying the correctness of inverse model neural networks. Our approach is to overapproximate a nonlinear, stochastic forward model with piecewise linear constraints and encode both the overapproximate forward model and the neural network inverse model as a mixed-integer program. We demonstrate this verification procedure on a real-world airplane fuel gauge case study. The ability to verify and consequently trust inverse model neural networks allows their use in a wide variety of contexts, from aerospace to medicine.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge