Variational Path Optimization of Linear Pentapods with a Simple Singularity Variety
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2019
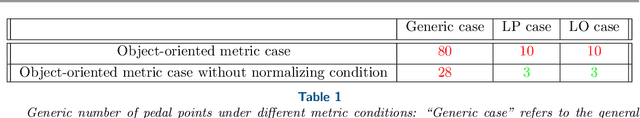


The class of linear pentapods with a simple singularity variety is obtained by imposing architectural restrictions on the design in such a way that the manipulators singularity variety is linear in orientation position variables. It turns out that such simplification leads to crucial computational advantages while maintaining the machines applications in some fundamental industrial tasks such as five axis milling and laser cutting. We assume that a path between a given start and end pose of the end effector is known which is singularity free and within the manipulators workspace. An optimization process of the initial path is proposed in such a way that the parallel robot increases its distance to the singularity loci while the motion is being smoothed. In our case the computation time of the optimization is improved as we are dealing with pentapods having simple singularity varieties allowing a closed form solution for the local exterma of the singularity distance function. Formally this process is called variational path optimization which is the systematic optimization of a path by manipulating its variations of energy and distance to the obstacle which in this case is the singularity variety. In this process some physical limits of the mechanical joints are also taken into account.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge