Variational framework for partially-measured physical system control: examples of vision neuroscience and optical random media
Paper and Code
Oct 25, 2021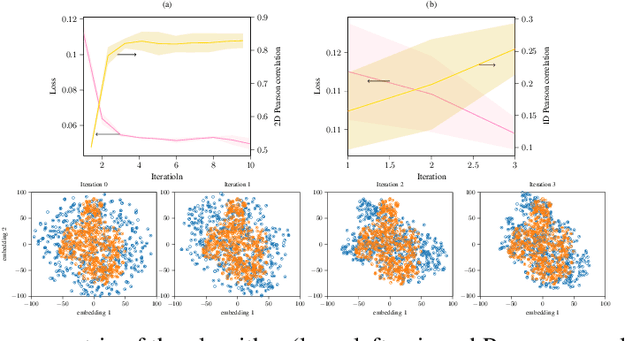
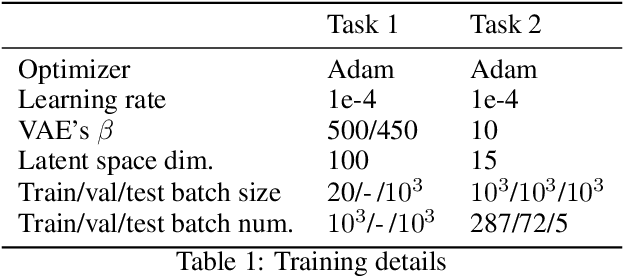
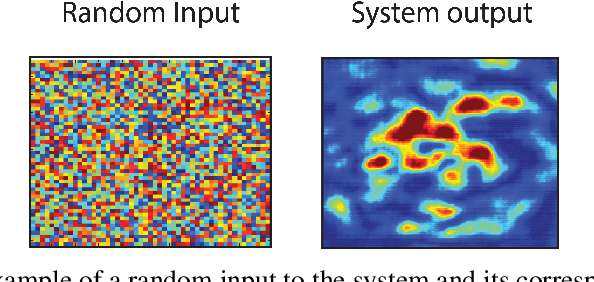

To characterize a physical system to behave as desired, either its underlying governing rules must be known a priori or the system itself be accurately measured. The complexity of full measurements of the system scales with its size. When exposed to real-world conditions, such as perturbations or time-varying settings, the system calibrated for a fixed working condition might require non-trivial re-calibration, a process that could be prohibitively expensive, inefficient and impractical for real-world use cases. In this work, we propose a learning procedure to obtain a desired target output from a physical system. We use Variational Auto-Encoders (VAE) to provide a generative model of the system function and use this model to obtain the required input of the system that produces the target output. We showcase the applicability of our method for two datasets in optical physics and neuroscience.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge