Variational Autoencoding the Lagrangian Trajectories of Particles in a Combustion System
Paper and Code
Dec 12, 2018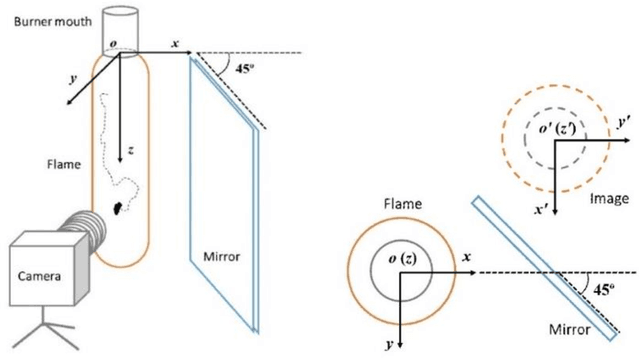

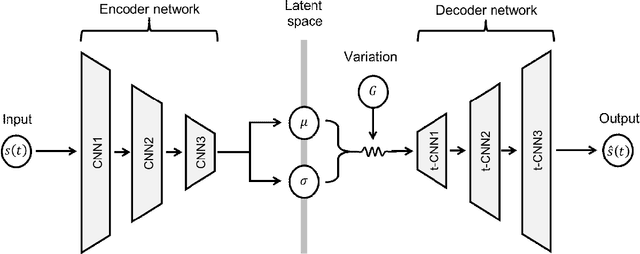
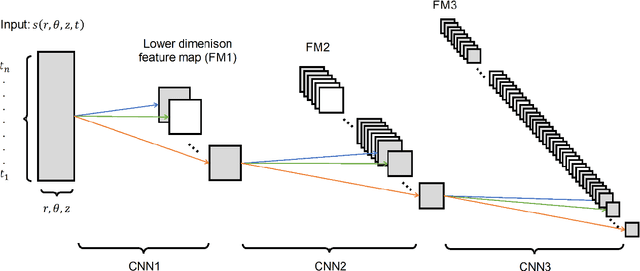
We introduce a deep learning method to simulate the motion of particles trapped in a chaotic recirculating flame. The Lagrangian trajectories of particles, captured using a high-speed camera and subsequently reconstructed in 3-dimensional space, were used to train a variational autoencoder (VAE) which comprises multiple layers of convolutional neural networks. We show that the trajectories, which are statistically representative of those determined in experiments, can be generated using the VAE network. The performance of our model is evaluated with respect to the accuracy and generalization of the outputs.
* 2nd version: typo corrected, corresponding author changed 19 pages, 9
figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge