Variance-adaptive confidence sequences by betting
Paper and Code
Oct 19, 2020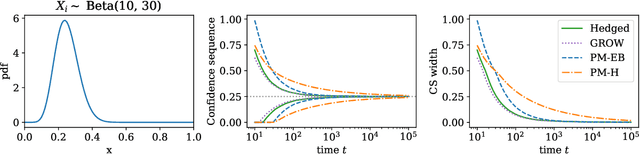
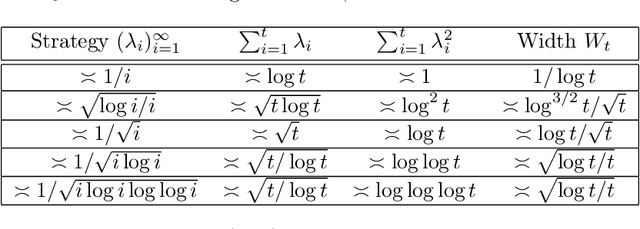
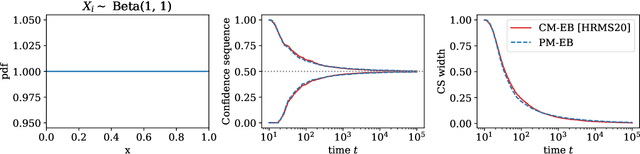

This paper derives confidence intervals (CI) and time-uniform confidence sequences (CS) for an unknown mean based on bounded observations. Our methods are based on a new general approach for deriving concentration bounds, that can be seen as a generalization (and improvement) of the classical Chernoff method. At its heart, it is based on deriving a new class of composite nonnegative martingales with initial value one, with strong connections to betting and the method of mixtures. We show how to extend these ideas to sampling without replacement. In all cases considered, the bounds are adaptive to the unknown variance, and empirically outperform competing approaches based on Hoeffding's or empirical Bernstein's inequalities and their recent supermartingale generalizations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge