Variable-lag Granger Causality for Time Series Analysis
Paper and Code
Dec 18, 2019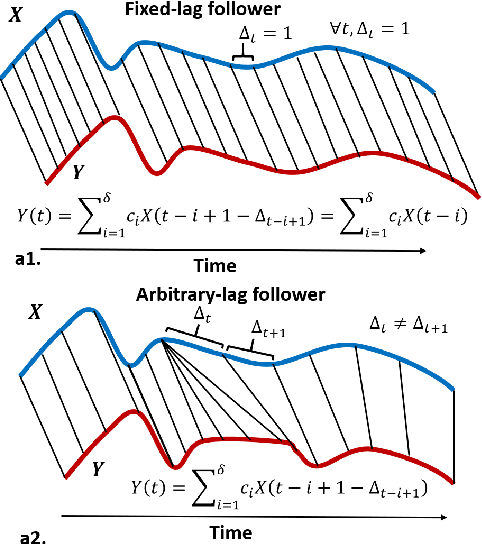
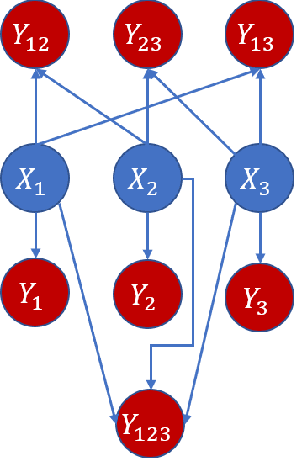
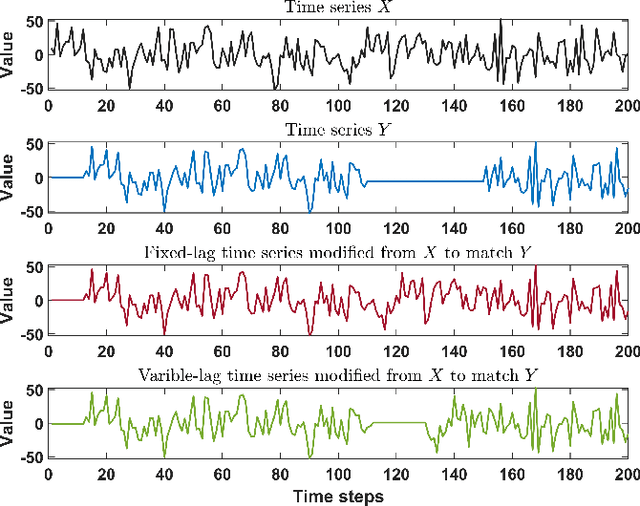

Granger causality is a fundamental technique for causal inference in time series data, commonly used in the social and biological sciences. Typical operationalizations of Granger causality make a strong assumption that every time point of the effect time series is influenced by a combination of other time series with a fixed time delay. However, the assumption of the fixed time delay does not hold in many applications, such as collective behavior, financial markets, and many natural phenomena. To address this issue, we develop variable-lag Granger causality, a generalization of Granger causality that relaxes the assumption of the fixed time delay and allows causes to influence effects with arbitrary time delays. In addition, we propose a method for inferring variable-lag Granger causality relations. We demonstrate our approach on an application for studying coordinated collective behavior and show that it performs better than several existing methods in both simulated and real-world datasets. Our approach can be applied in any domain of time series analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge