User-centered Evaluation of Popularity Bias in Recommender Systems
Paper and Code
Mar 10, 2021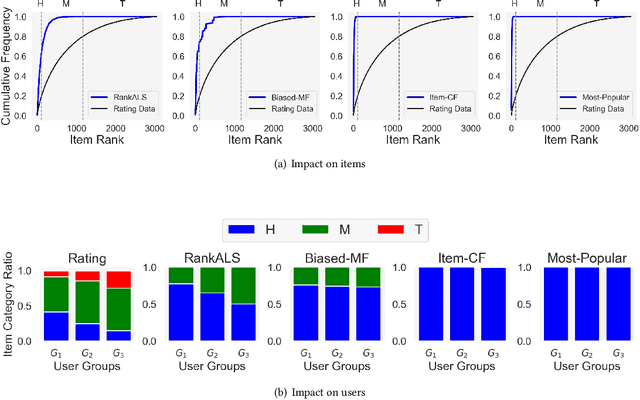
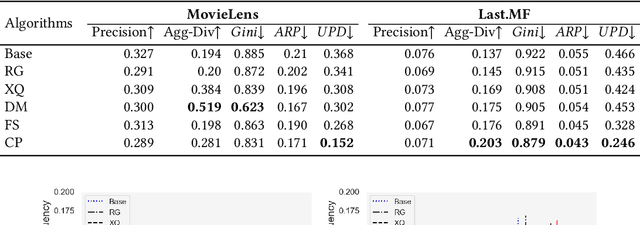
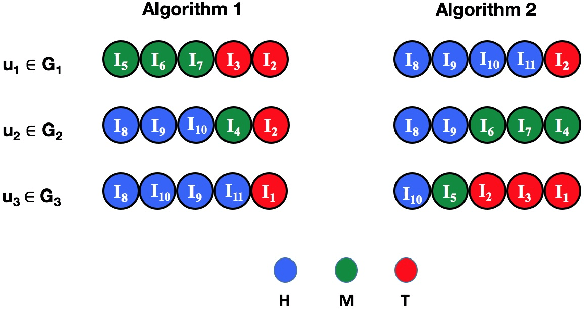
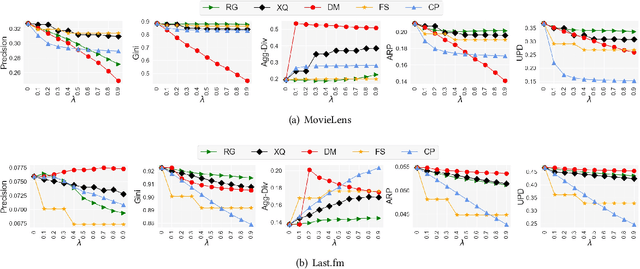
Recommendation and ranking systems are known to suffer from popularity bias; the tendency of the algorithm to favor a few popular items while under-representing the majority of other items. Prior research has examined various approaches for mitigating popularity bias and enhancing the recommendation of long-tail, less popular, items. The effectiveness of these approaches is often assessed using different metrics to evaluate the extent to which over-concentration on popular items is reduced. However, not much attention has been given to the user-centered evaluation of this bias; how different users with different levels of interest towards popular items are affected by such algorithms. In this paper, we show the limitations of the existing metrics to evaluate popularity bias mitigation when we want to assess these algorithms from the users' perspective and we propose a new metric that can address these limitations. In addition, we present an effective approach that mitigates popularity bias from the user-centered point of view. Finally, we investigate several state-of-the-art approaches proposed in recent years to mitigate popularity bias and evaluate their performances using the existing metrics and also from the users' perspective. Our experimental results using two publicly-available datasets show that existing popularity bias mitigation techniques ignore the users' tolerance towards popular items. Our proposed user-centered method can tackle popularity bias effectively for different users while also improving the existing metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge